Exploring alternative treatments for Helicobacter pylori infection
- PMID: 24587621
- PMCID: PMC3925854
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1450
Exploring alternative treatments for Helicobacter pylori infection
Abstract
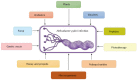
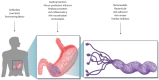
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a successful pathogen that can persist in the stomach of an infected person for their entire life. It provokes chronic gastric inflammation that leads to the development of serious gastric diseases such as peptic ulcers, gastric cancer and Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. It is known that these ailments can be avoided if the infection by the bacteria can be prevented or eradicated. Currently, numerous antibiotic-based therapies are available. However, these therapies have several inherent problems, including the appearance of resistance to the antibiotics used and associated adverse effects, the risk of re-infection and the high cost of antibiotic therapy. The delay in developing a vaccine to prevent or eradicate the infection has furthered research into new therapeutic approaches. This review summarises the most relevant recent studies on vaccine development and new treatments using natural resources such as plants, probiotics and nutraceuticals. In addition, novel alternatives based on microorganisms, peptides, polysaccharides, and intragastric violet light irradiation are presented. Alternative therapies have not been effective in eradicating the bacteria but have been shown to maintain low bacterial levels. Nevertheless, some of them are useful in preventing the adverse effects of antibiotics, modulating the immune response, gastroprotection, and the general promotion of health. Therefore, those agents can be used as adjuvants of allopathic anti-H. pylori eradication therapy.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; Natural products; Nutraceuticals; Probiotics; Treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Probiotics in Managing of Helicobacter Pylori Infection: A Review.Drug Res (Stuttg). 2017 Feb;67(2):88-93. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-116441. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2017. PMID: 27824431 Review.
-
Novel and Effective Therapeutic Regimens for Helicobacter pylori in an Era of Increasing Antibiotic Resistance.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 May 5;7:168. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00168. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28529929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative therapies for Helicobacter pylori: probiotics and phytomedicine.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2011 Nov;63(2):153-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2011.00865.x. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 22077218 Review.
-
Overview of the phytomedicine approaches against Helicobacter pylori.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 May 21;20(19):5594-609. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i19.5594. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24914319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Are probiotics useful for therapy of Helicobacter pylori diseases?Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019 Jun;64:99-108. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2019.02.010. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31174707 Review.
Cited by
-
Low dose furazolidone for eradication of H- pylori instead of clarithromycin: a clinical trial.Glob J Health Sci. 2014 Aug 31;7(1):235-9. doi: 10.5539/gjhs.v7n1p235. Glob J Health Sci. 2014. PMID: 25560342 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Flavodoxins as Novel Therapeutic Targets against Helicobacter pylori and Other Gastric Pathogens.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 10;21(5):1881. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051881. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32164177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Native Gastric Mucus on in vivo Hybridization Therapies Directed at Helicobacter pylori.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2015 Dec 8;4(12):e269. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2015.46. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2015. PMID: 26645765 Free PMC article.
-
Consumption of a Gelatin Supplemented with the Probiotic Strain Limosilactobacillus fermentum UCO-979C Prevents Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Young Adult Population Achieved.Foods. 2022 Jun 7;11(12):1668. doi: 10.3390/foods11121668. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35741866 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic susceptibility, heteroresistance, and updated treatment strategies in Helicobacter pylori infection.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017 Jul 28;11:2209-2220. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S136240. eCollection 2017. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017. PMID: 28814829 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clyne M, Dolan B, Reeves EP. Bacterial factors that mediate colonization of the stomach and virulence of Helicobacter pylori. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007;268:135–143. - PubMed
-
- Dunn BE, Campbell GP, Perez-Perez GI, Blaser MJ. Purification and characterization of urease from Helicobacter pylori. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:9464–9469. - PubMed
-
- Harris PR, Mobley HL, Perez-Perez GI, Blaser MJ, Smith PD. Helicobacter pylori urease is a potent stimulus of mononuclear phagocyte activation and inflammatory cytokine production. Gastroenterology. 1996;111:419–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

