Clinical approaches to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 24587650
- PMCID: PMC3930971
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1712
Clinical approaches to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
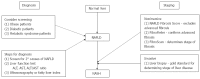
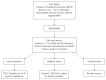
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) ranges from simple steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), leading to fibrosis and potentially cirrhosis, and it is one of the most common causes of liver disease worldwide. NAFLD is associated with other medical conditions such as metabolic syndrome, obesity, cardiovascular disease and diabetes. NASH can only be diagnosed through liver biopsy, but noninvasive techniques have been developed to identify patients who are most likely to have NASH or fibrosis, reducing the need for liver biopsy and risk to patients. Disease progression varies between individuals and is linked to a number of risk factors. Mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis are associated with diet and lifestyle, influx of free fatty acids to the liver from adipose tissue due to insulin resistance, hepatic oxidative stress, cytokines production, reduced very low-density lipoprotein secretion and intestinal microbiome. Weight loss through improved diet and increased physical activity has been the cornerstone therapy of NAFLD. Recent therapies such as pioglitazone and vitamin E have been shown to be beneficial. Omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and statins may offer additional benefits. Bariatric surgery should be considered in morbidly obese patients. More research is needed to assess the impact of these treatments on a long-term basis. The objective of this article is to briefly review the diagnosis, management and treatment of this disease in order to aid clinicians in managing these patients.
Keywords: Cirrhosis; Diagnosis; Management; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Pathogenesis; Steatohepatitis; Steatosis; Treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Clark JM, Diehl AM. Hepatic steatosis and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Diab Rep. 2002;2:210–215. - PubMed
-
- Bedogni G, Miglioli L, Masutti F, Tiribelli C, Marchesini G, Bellentani S. Prevalence of and risk factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the Dionysos nutrition and liver study. Hepatology. 2005;42:44–52. - PubMed
-
- Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC, Grundy SM, Hobbs HH. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology. 2004;40:1387–1395. - PubMed
-
- Vernon G, Baranova A, Younossi ZM. Systematic review: the epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;34:274–285. - PubMed
-
- Machado M, Marques-Vidal P, Cortez-Pinto H. Hepatic histology in obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery. J Hepatol. 2006;45:600–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

