Modulation of hepatic steatosis by dietary fatty acids
- PMID: 24587652
- PMCID: PMC3930973
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1746
Modulation of hepatic steatosis by dietary fatty acids
Abstract
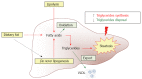
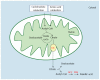
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) describes a range of conditions caused by fat deposition within liver cells. Liver fat content reflects the equilibrium between several metabolic pathways involved in triglyceride synthesis and disposal, such as lipolysis in adipose tissue and de novo lipogenesis, triglyceride esterification, fatty acid oxidation and very-low-density lipoprotein synthesis/secretion in hepatic tissue. In particular, it has been demonstrated that hepatic de novo lipogenesis plays a significant role in NAFLD pathogenesis. It is widely known that the fatty acid composition of the diet influences hepatic lipogenesis along with other metabolic pathways. Therefore, dietary fat may not only be involved in the pathogenesis of hepatic steatosis, but may also prevent and/or reverse hepatic fat accumulation. In this review, major data from the literature about the role of some dietary fats as a potential cause of hepatic fat accumulation or as a potential treatment for NAFLD are described. Moreover, biochemical mechanisms responsible for an increase or decrease in hepatic lipid content are critically analyzed. It is noteworthy that both quantitative and qualitative aspects of dietary fat influence triglyceride deposition in the liver. A high-fat diet or the dietary administration of conjugated linoleic acids induced hepatic steatosis. In contrast, supplementation of the diet with krill oil or pine nut oil helped in the prevention and/or in the treatment of steatotic liver. Quite interesting is the "case" of olive oil, since several studies have often provided different and/or conflicting results in animal models.
Keywords: Fatty acids; Hepatic steatosis; Lipogenesis; Non-alcoholic fatty liver.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of trans-fatty acids on TAG regulation in mice depend on dietary unsaturated fatty acids.Br J Nutr. 2016 Aug;116(4):611-20. doi: 10.1017/S0007114516002415. Br J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27464460
-
Comparative study of the modulation of fructose/sucrose-induced hepatic steatosis by mixed lipid formulations varying in unsaturated fatty acid content.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2015 Nov 14;12:41. doi: 10.1186/s12986-015-0038-x. eCollection 2015. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26583036 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary walnut oil modulates liver steatosis in the obese Zucker rat.Eur J Nutr. 2014;53(2):645-60. doi: 10.1007/s00394-013-0573-z. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Eur J Nutr. 2014. PMID: 23942585 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of hepatic triglyceride accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.J Gastroenterol. 2013 Apr;48(4):434-41. doi: 10.1007/s00535-013-0758-5. Epub 2013 Feb 9. J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23397118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fructose as a key player in the development of fatty liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Feb 28;19(8):1166-72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1166. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23482247 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sodium fluorocitrate having inhibitory effect on fatty acid uptake ameliorates high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in C57BL/6J mice.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 28;9(1):17839. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54476-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31780766 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional programming by maternal diet alters offspring lipid metabolism in a marine teleost.Fish Physiol Biochem. 2022 Jun;48(3):535-553. doi: 10.1007/s10695-022-01069-1. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35399145
-
Multi-Omics Reveals Inhibitory Effect of Baicalein on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 15;13:925349. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.925349. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35784718 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance Exercise Regulates Hepatic Lipolytic Factors as Effective as Aerobic Exercise in Obese Mice.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 10;17(22):8307. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17228307. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33182720 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional Characterization, Antioxidant, and Lipid-Lowering Effects of Yellow Mombin (Spondias mombin) Supplemented to Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet.Foods. 2022 Oct 2;11(19):3064. doi: 10.3390/foods11193064. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36230142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lewis JR, Mohanty SR. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a review and update. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55:560–578. - PubMed
-
- Day CP, James OF. Steatohepatitis: a tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology. 1998;114:842–845. - PubMed
-
- Puri P, Baillie RA, Wiest MM, Mirshahi F, Choudhury J, Cheung O, Sargeant C, Contos MJ, Sanyal AJ. A lipidomic analysis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2007;46:1081–1090. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

