Increased susceptibility to Trichuris muris infection and exacerbation of colitis in Mdr1a-/- mice
- PMID: 24587657
- PMCID: PMC3930978
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1797
Increased susceptibility to Trichuris muris infection and exacerbation of colitis in Mdr1a-/- mice
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the influence of Trichuris muris (T. muris) infection in a mouse model of genetic susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease, Mdr1a-/-.
Methods: Mdr1a-/- mice were housed under specific pathogen free conditions to slow the development of colitis and compared to congenic FVB controls. Mice were infected with approximately 200 embryonated ova from T. muris and assessed for worm burden and histological and functional markers of gut inflammation on day 19 post infection.
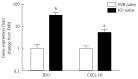
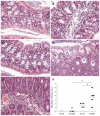
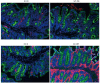
Results: Mdr1a-/- mice exhibited a marked increase in susceptibility to T. muris infection with a 10-fold increase in colonic worm count by day 19 pi compared to FVB controls. Prior to infection, Mdr1a-/- exhibited low-level mucosal inflammation with evidence of an enhanced Th1 environment. T. muris infection accelerated the progression of colitis in Mdr1a-/- as evidenced by marked increases in several indicators including histological damage score, mucosal CD⁺ T-cell and DC infiltration and dramatically increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Conclusion: These data provide further evidence of the complex interaction between T. muris and an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)-susceptible host which may have relevance to the application of helminth therapy in the treatment of human IBD.
Keywords: Colitis; Helminth; Inflammatory bowel disease; Mdr1a; P-glycoprotein.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genetic analysis of the Trichuris muris-induced model of colitis reveals QTL overlap and a novel gene cluster for establishing colonic inflammation.BMC Genomics. 2013 Feb 26;14:127. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-127. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23442222 Free PMC article.
-
Colonic transcriptional profiling in resistance and susceptibility to trichuriasis: phenotyping a chronic colitis and lessons for iatrogenic helminthosis.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010 Dec;16(12):2065-79. doi: 10.1002/ibd.21326. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010. PMID: 20687192
-
Critical role for P-glycoprotein expression in hematopoietic cells in the FVB.Mdr1a(-/-) model of colitis.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011 Dec;53(6):666-73. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31822860f1. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21681110 Free PMC article.
-
The mdr1a-/- mouse model of spontaneous colitis: a relevant and appropriate animal model to study inflammatory bowel disease.Immunol Res. 2005;31(2):151-9. doi: 10.1385/IR:31:2:151. Immunol Res. 2005. PMID: 15778512 Review.
-
Another decade of Trichuris muris research: An update and application of key discoveries.Adv Parasitol. 2023;121:1-63. doi: 10.1016/bs.apar.2023.05.002. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Adv Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 37474238 Review.
Cited by
-
Intestinal helminth infection drives carcinogenesis in colitis-associated colon cancer.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Sep 22;13(9):e1006649. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006649. eCollection 2017 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28938014 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaceutical Potential of Remedial Plants and Helminths for Treating Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jun 21;17(7):819. doi: 10.3390/ph17070819. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunity to gastrointestinal nematode infections.Mucosal Immunol. 2018 Mar;11(2):304-315. doi: 10.1038/mi.2017.113. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Mucosal Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29297502 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of helminths in autoimmune diseases: helminth-derived immune-regulators and immune balance.Parasitol Res. 2017 Aug;116(8):2065-2074. doi: 10.1007/s00436-017-5544-5. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Parasitol Res. 2017. PMID: 28664463 Review.
-
P-glycoprotein multidrug transporter in inflammatory bowel diseases: More questions than answers.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Mar 7;23(9):1513-1520. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i9.1513. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28321153 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cliffe LJ, Grencis RK. The Trichuris muris system: a paradigm of resistance and susceptibility to intestinal nematode infection. Adv Parasitol. 2004;57:255–307. - PubMed
-
- Else KJ. Have gastrointestinal nematodes outwitted the immune system? Parasite Immunol. 2005;27:407–415. - PubMed
-
- Summers RW, Elliott DE, Urban JF, Thompson RA, Weinstock JV. Trichuris suis therapy for active ulcerative colitis: a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:825–832. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

