Stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligo-recurrence within the nodal area from colorectal cancer
- PMID: 24587675
- PMCID: PMC3934470
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.2005
Stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligo-recurrence within the nodal area from colorectal cancer
Abstract
Recurrence of colorectal cancer (CRC) often presents as solitary metastases, oligometastases or oligo-recurrence. Surgical resection became the preferred treatment for patients with CRC lung and hepatic metastases. However, surgical treatment for oligo-recurrence within nodal area is not a widely accepted treatment due to due to their relative rarity and high postoperative morbidity. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) is one of the emerging radiation treatment techniques in which a high radiation dose can be delivered to the tumor. High-dose SBRT can ablate the tumor with an efficacy similar to that achieved with surgery, especially for small tumors. However, there have been very few studies on SBRT for oligo-recurrence within nodal area, although several studies have evaluated the role of SBRT in the treatment of liver and lung metastases from CRC. This article reviews the current clinical status of and treatment methods for oligo-recurrence within nodal area from CRC, with particular emphasis on SBRT.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Lymph node; Oligo-recurrence; Oligometastases; Stereotactic radiotherapy.
Figures
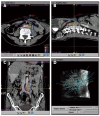
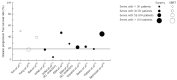
Similar articles
-
Additional chemotherapy improved local control and overall survival after stereotactic body radiation therapy for patients with oligo-recurrence.Radiat Oncol. 2018 Apr 23;13(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13014-018-1031-0. Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29688858 Free PMC article.
-
Survival and prognostic factors in 321 patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligo-metastases.Radiother Oncol. 2015 Feb;114(2):155-60. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2014.12.003. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Radiother Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25583567
-
Role of stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastasis from colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Apr 21;20(15):4220-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4220. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24764660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung metastases as oligo-recurrence: a single institutional study.J Radiat Res. 2016 Jan;57(1):55-61. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrv063. Epub 2015 Oct 22. J Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 26494115 Free PMC article.
-
[Local ablative radiotherapy of oligometastatic colorectal cancer].Radiologe. 2017 Feb;57(2):105-110. doi: 10.1007/s00117-016-0201-z. Radiologe. 2017. PMID: 28054139 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver oligo-recurrence and oligo-progression from various tumors.Radiat Oncol J. 2017 Jun;35(2):172-179. doi: 10.3857/roj.2017.00024. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Radiat Oncol J. 2017. PMID: 28712274 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy for the treatment of lymph node metastases: a retrospective mono-institutional study in a large cohort of patients.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 3;13:1163213. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1163213. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37601675 Free PMC article.
-
Octaarginine-modified gold nanoparticles enhance the radiosensitivity of human colorectal cancer cell line LS180 to megavoltage radiation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Jun 19;13:3541-3552. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S161157. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29950834 Free PMC article.
-
A postoperative scoring system for post-hepatectomy early recurrence of colorectal liver metastases.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 15;8(60):102531-102539. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20934. eCollection 2017 Nov 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29254268 Free PMC article.
-
The evolving role of radiation therapy as treatment for liver metastases.J Natl Cancer Cent. 2022 Jul 19;2(3):183-187. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2022.06.004. eCollection 2022 Sep. J Natl Cancer Cent. 2022. PMID: 39036451 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Sung J. Colorectal cancer screening: its time for action in Asia. Cancer Detect Prev. 2007;31:1–2. - PubMed
-
- Sung JJ, Lau JY, Goh KL, Leung WK. Increasing incidence of colorectal cancer in Asia: implications for screening. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6:871–876. - PubMed
-
- Delpero JR, Pol B, Le Treut P, Bardou VJ, Moutardier V, Hardwigsen J, Granger F, Houvenaeghel G. Surgical resection of locally recurrent colorectal adenocarcinoma. Br J Surg. 1998;85:372–376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

