ZD 7288, an HCN channel blocker, attenuates chronic visceral pain in irritable bowel syndrome-like rats
- PMID: 24587682
- PMCID: PMC3934480
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.2091
ZD 7288, an HCN channel blocker, attenuates chronic visceral pain in irritable bowel syndrome-like rats
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of ZD 7288, a hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel blocker, on rats with chronic visceral pain.
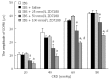
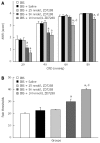
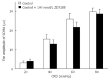
Methods: Rats with visceral hypersensitivity were generated using neonatal colon irritation during postnatal days 8-15 as described previously. Visceral hypersensitivity was evaluated using electromyographic (EMG) responses of abdominal external oblique muscles to 20-80 mmHg colorectal distentions (CRD). Abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) scores and pain thresholds were also detected in adult rats. Different doses of ZD 7288 (25, 50, and 100 nmol/L) were intrathecally administered in rats to study the role of spinal HCN channel in chronic visceral hypersensitivity.
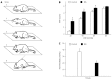
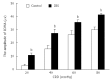
Results: EMG responses to 20-80 mmHg CRD and AWR scores under 20-60 mmHg CRD significantly increased in rats with visceral hypersensitivity compared to control rats (P < 0.05). The pain threshold in rats with visceral hypersensitivity significantly decreased compared to control rats (P < 0.05). Treatment with 50-100 nmol/L ZD 7288 significantly inhibited EMG responses (16%-62%, 80-20 mmHg CRD, P < 0.05) and AWR scores (24%-37%, 40-20 mmHg CRD, P < 0.05; 12%-61%, 80-20 mmHg CRD, P < 0.05, respectively), and significantly increased pain thresholds (32%-77%, P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Spinal HCN channels may play an important role in chronic visceral hypersensitivity.
Keywords: Abdominal withdrawal reflex; Electromyography; Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel; Irritable bowel syndrome; Visceral hypersensitivity; ZD 7288.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Schisandra chinensis reverses visceral hypersensitivity in a neonatal-maternal separated rat model.Phytomedicine. 2012 Mar 15;19(5):402-8. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2011.11.013. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Phytomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22230486 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture alleviates stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity through an opioid system in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Dec 28;18(48):7201-11. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7201. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23326125 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of electroacupuncture on corticotropin-releasing hormone in rats with chronic visceral hypersensitivity.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 21;21(23):7181-90. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i23.7181. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26109804 Free PMC article.
-
Transient receptor potential ion channel function in sensory transduction and cellular signaling cascades underlying visceral hypersensitivity.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):G635-G648. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00401.2016. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28385695 Review.
-
Guanylate cyclase-C agonists as peripherally acting treatments of chronic visceral pain.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Feb;43(2):110-122. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2021.11.002. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 34865885 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased HCN2 channel expression attenuates neuropathic pain by inhibiting pro-inflammatory reactions and NF-κB activation in mice.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019 Jan 1;12(1):154-163. eCollection 2019. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31933729 Free PMC article.
-
Pomegranate Mesocarp against Colitis-Induced Visceral Pain in Rats: Effects of a Decoction and Its Fractions.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 17;21(12):4304. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124304. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32560291 Free PMC article.
-
Deepening the Mechanisms of Visceral Pain Persistence: An Evaluation of the Gut-Spinal Cord Relationship.Cells. 2020 Jul 24;9(8):1772. doi: 10.3390/cells9081772. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32722246 Free PMC article.
-
Acute visceral pain relief mediated by A3AR agonists in rats: involvement of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels.Pain. 2020 Sep 1;161(9):2179-2190. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001905. Pain. 2020. PMID: 32379223 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonic Anhydrase IV Selective Inhibitors Counteract the Development of Colitis-Associated Visceral Pain in Rats.Cells. 2021 Sep 26;10(10):2540. doi: 10.3390/cells10102540. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Camilleri M. Current and future pharmacological treatments for diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013;14:1151–1160. - PubMed
-
- Zhou EH, Liu HR, Wu HG, Shi Y, Wang XM, Tan LY, Yao LQ, Zhong YS, Jiang Y, Zhang LL. Suspended moxibustion relieves chronic visceral hyperalgesia via serotonin pathway in the colon. Neurosci Lett. 2009;451:144–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

