A new automated way to measure polyethylene wear in THA using a high resolution CT scanner: method and analysis
- PMID: 24587727
- PMCID: PMC3920851
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/528407
A new automated way to measure polyethylene wear in THA using a high resolution CT scanner: method and analysis
Abstract
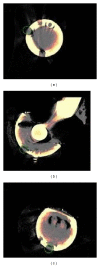
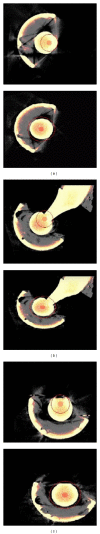
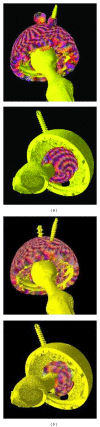
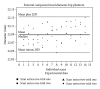
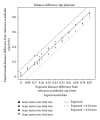
As the most advantageous total hip arthroplasty (THA) operation is the first, timely replacement of only the liner is socially and economically important because the utilization of THA is increasing as younger and more active patients are receiving implants and they are living longer. Automatic algorithms were developed to infer liner wear by estimating the separation between the acetabular cup and femoral component head given a computed tomography (CT) volume. Two series of CT volumes of a hip phantom were acquired with the femoral component head placed at 14 different positions relative to the acetabular cup. The mean and standard deviation (SD) of the diameter of the acetabular cup and femoral component head, in addition to the range of error in the expected wear values and the repeatability of all the measurements, were calculated. The algorithms resulted in a mean (± SD) for the diameter of the acetabular cup of 54.21 (± 0.011) mm and for the femoral component head of 22.09 (± 0.02) mm. The wear error was ± 0.1 mm and the repeatability was 0.077 mm. This approach is applicable clinically as it utilizes readily available computed tomography imaging systems and requires only five minutes of human interaction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vivo and ex vivo measurement of polyethylene wear in total hip arthroplasty: comparison of measurements using a CT algorithm, a coordinate-measuring machine, and a micrometer.Acta Orthop. 2014 Jun;85(3):271-5. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2014.913225. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Acta Orthop. 2014. PMID: 24758322 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparative study on association between femoral head size and linear wear rate of highly cross-linked polyethylene liner].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Nov;28(11):1333-7. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25639045 Chinese.
-
[Comparative study on high cross-linked and traditional polyethylene cup liners in total hip arthroplasty].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Dec;27(12):1414-8. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24640355 Chinese.
-
Serial measurement of polyethylene wear of well-fixed cementless metal-backed acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty: an over 10 year follow-up study.Artif Organs. 2000 Sep;24(9):746-51. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1594.2000.06571-2.x. Artif Organs. 2000. PMID: 11012546
-
New polymer materials in total hip arthroplasty. Evaluation with radiostereometry, bone densitometry, radiography and clinical parameters.Acta Orthop Suppl. 2005 Feb;76(315):3-82. Acta Orthop Suppl. 2005. PMID: 15790289 Review.
Cited by
-
Prosthetic liner wear in total hip replacement: a longitudinal 13-year study with computed tomography.Skeletal Radiol. 2018 Jun;47(6):883-887. doi: 10.1007/s00256-018-2878-8. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Skeletal Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29362844 Free PMC article.
-
"Great balls on fire:" known algorithm with a new instrument?Acta Orthop. 2020 Dec;91(6):621-623. doi: 10.1080/17453674.2020.1840029. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Acta Orthop. 2020. PMID: 33143497 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Is the use of thin, highly cross-linked polyethylene liners safe in total hip arthroplasty?Int Orthop. 2016 Apr;40(4):681-6. doi: 10.1007/s00264-015-2841-4. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Int Orthop. 2016. PMID: 26130285
-
A CT method for following patients with both prosthetic replacement and implanted tantalum beads: preliminary analysis with a pelvic model and in seven patients.J Orthop Surg Res. 2016 Feb 24;11:27. doi: 10.1186/s13018-016-0360-7. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 26911571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karrholm J, Frech W, Nilsson K-G, Snorrason F. Increased metal release from cemented femoral components made of titanium alloy: 19 hip prostheses followed with radiostereometry (RSA) Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica. 1994;65(6):599–604. - PubMed
-
- Harris WH. Osteolysis and particle disease in hip replacement: a review. Acta Orthop Scand. 1994;65(1):113–123. - PubMed
-
- Thomas GER, Simpson DJ, Mehmood S, et al. The seven-year wear of highly cross-linked polyethylene in total hip arthroplasty: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial using radiostereometric analysis. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery A. 2011;93(8):716–722. - PubMed
-
- Dai X, Omori H, Okumura Y, et al. Serial measurement of polyethylene wear of well-fixed cementless metal-backed acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty: An over 10 year follow-up study. Artificial Organs. 2000;24(9):746–751. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

