Molecular divergence and species delimitation of the cultivated oyster mushrooms: integration of IGS1 and ITS
- PMID: 24587752
- PMCID: PMC3918722
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/793414
Molecular divergence and species delimitation of the cultivated oyster mushrooms: integration of IGS1 and ITS
Abstract
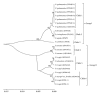
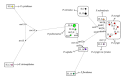
Identification of edible mushrooms particularly Pleurotus genus has been restricted due to various obstacles. The present study attempted to use the combination of two variable regions of IGS1 and ITS for classifying the economically cultivated Pleurotus species. Integration of the two regions proved a high ability that not only could clearly distinguish the species but also served sufficient intraspecies variation. Phylogenetic tree (IGS1+ITS) showed seven distinct clades, each clade belonging to a separate species group. Moreover, the species differentiation was tested by AMOVA and the results were reconfirmed by presenting appropriate amounts of divergence (91.82% among and 8.18% within the species). In spite of achieving a proper classification of species by combination of IGS1 and ITS sequences, the phylogenetic tree showed the misclassification of the species of P. nebrodensis and P. eryngii var. ferulae with other strains of P. eryngii. However, the constructed median joining (MJ) network could not only differentiate between these species but also offer a profound perception of the species' evolutionary process. Eventually, due to the sufficient variation among and within species, distinct sequences, simple amplification, and location between ideal conserved ribosomal genes, the integration of IGS1 and ITS sequences is recommended as a desirable DNA barcode.
Figures
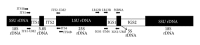

References
-
- Wang Y, Zeng F, Hon CC, Zhang Y, Leung FCC. The mitochondrial genome of the Basidiomycete fungus Pleurotus ostreatus (oyster mushroom) FEMS Microbiology Letters. 2008;280(1):34–41. - PubMed
-
- Adebayo EA, Oloke JK, Yadav A, Barooah M, Bora TC. Improving yield performance of Pleurotus pulmonarius through hyphal anastomosis fusion of dikaryons. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2013;29:1029–1037. - PubMed
-
- Adejumo TO, Awosanya OB. Proximate and mineral composition of four edible mushroom species from South Western Nigeria. African Journal of Biotechnology. 2005;4(10):1084–1088.
-
- Zervakis G, Balis C. A pluralistic approach in the study of Pleurotus species with emphasis on compatibility and physiology of the European morphotaxa. Mycological Research. 1996;100(6):717–731.
-
- Ravash R, Shiran B, Alavi AA, Bayat F, Rajaee S, Zervakis GI. Genetic variability and molecular phylogeny of Pleurotus eryngii species-complex isolates from Iran, and notes on the systematics of Asiatic populations. Mycological Progress. 2010;9(2):181–194.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

