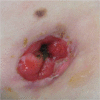
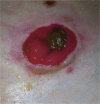
Immunoglobulin therapy for refractory Crohn's disease
- PMID: 24587823
- PMCID: PMC3903086
- DOI: 10.1177/1756283X13504728
Immunoglobulin therapy for refractory Crohn's disease
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; immunoglobulin; inflammatory bowel disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distinct patterns of immunoglobulin classes and IgG subclasses of autoantibodies in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996 Jun;8(6):579-84. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199606000-00016. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996. PMID: 8823574
-
Immunoglobulin G subclasses in Crohn's disease with and without bowel resection.Sb Ved Pr Lek Fak Karlovy Univerzity Hradci Kralove. 1993;36(3):139-47. Sb Ved Pr Lek Fak Karlovy Univerzity Hradci Kralove. 1993. PMID: 8159910
-
The immune competence of patients with inflammatory bowel disease.Gut. 1974 Mar;15(3):213-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.3.213. Gut. 1974. PMID: 4841278 Free PMC article.
-
Management of inflammatory bowel disease with infliximab and other anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapies.BioDrugs. 2010 Dec 14;24 Suppl 1:3-14. doi: 10.2165/11586290-000000000-00000. BioDrugs. 2010. PMID: 21175228 Review.
-
CARD15 mutations in Dutch familial and sporadic inflammatory bowel disease and an overview of European studies.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 Jun;19(6):449-59. doi: 10.1097/01.meg.0000236887.44214.6a. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. PMID: 17489054 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent insights into the molecular pathogenesis of Crohn's disease: a review of emerging therapeutic targets.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2016 Mar 15;9:59-70. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S53381. eCollection 2016. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27042137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infliximab is effective in the treatment of ulcerative colitis with dermatomyositis: A case report.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Dec 14;26(46):7425-7435. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i46.7425. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33362394 Free PMC article.
-
IgG and Fcγ Receptors in Intestinal Immunity and Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 12;10:805. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00805. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31031776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastrointestinal Manifestations in X-linked Agammaglobulinemia.J Clin Immunol. 2017 Apr;37(3):287-294. doi: 10.1007/s10875-017-0374-x. Epub 2017 Feb 24. J Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28236219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abolhassani H., Sadaghiani M., Aghamohammadi A., Ochs H., Rezaei N. (2012) Home-based subcutaneous immunoglobulin versus hospital-based intravenous immunoglobulin in treatment of primary antibody deficiencies: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Immunol 32: 1180–1192 - PubMed
-
- Berger M., Murphy E., Riley P., Bergman G. and VIRTUE Trial Investigators (2010) Improved quality of life, immunoglobulin G levels, and infection rates in patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases during self-treatment with subcutaneous immunoglobulin G. South Med J 103: 856–863 - PubMed
-
- Chapel H., Spickett G., Ericson D., Engl W., Eibl M., Bjorkander J. (2000) The comparison of the efficacy and safety of intravenous versus subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement therapy. J Clin Immunol 20: 94–100 - PubMed
-
- Danieli M., Pettinari L., Moretti R., Logullo F., Gabrielli A. (2011) Subcutaneous immunoglobulin in polymyositis and dermatomyositis: a novel application. Autoimmun Rev 10: 144–149 - PubMed
-
- Gardulf A. (2007) Immunoglobulin treatment for primary antibody deficiencies: advantages of the subcutaneous route. Biodrugs 21: 105–116 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources