Dopamine D2R Agonist-Induced Cardiovascular Effects in Healthy Male Subjects: Potential Implications in Clinical Settings
- PMID: 24587918
- PMCID: PMC3920609
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/956353
Dopamine D2R Agonist-Induced Cardiovascular Effects in Healthy Male Subjects: Potential Implications in Clinical Settings
Abstract
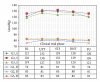
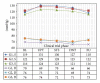
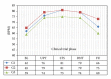
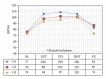
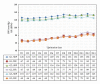
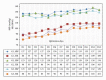
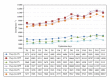
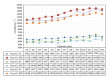
Dopamine D2 receptor agonists represent a first line treatment option in young patients with signs and symptoms of idiopathic Parkinson's disease. An association between the use of D2 receptor agonists in Parkinson's disease patients and heart failure has been reported. The identification of the underlying mechanism is needed to minimize the resultant cardiovascular morbidity. In a phase I clinical trial, a D2 receptor agonist (pramipexole) was administered to 52 healthy male subjects following a dose escalation scheme. Serial measurements of resting blood pressure, heart rate, and derived parameters including pulse pressure, pulsatile stress, and rate pressure product were analysed. Statistically significant and clinically relevant increases in most of the assessed parameters were found. Ten subjects were removed prematurely from the trial because of clinically significant increases in blood pressure and/or heart rate requiring immediate intervention with IV rescue medications including a selective β -1 blocker. The observed drug-related changes in vital signs were of clinical relevance and might explain some of the cardiovascular morbidity reported in patients receiving D2 receptor agonist in clinical settings. We suggest that the additional use of a β -1 blocking agent might mitigate the risk of cardiovascular morbidity among patients receiving long-term D2 receptor agonists.
Figures
References
-
- Missale C, Russel Nash S, Robinson SW, Jaber M, Caron MG. Dopamine receptors: from structure to function. Physiological Reviews. 1998;78(1):189–225. - PubMed
-
- Hussain T, Lokhandwala MF. Renal dopamine receptors and hypertension. Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2003;228(2):134–142. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu J-M, Gainetdinov RR. The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacological Reviews. 2011;63(1):182–217. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

