Prevalence of immediate-type food allergy in early childhood in seoul
- PMID: 24587949
- PMCID: PMC3936041
- DOI: 10.4168/aair.2014.6.2.131
Prevalence of immediate-type food allergy in early childhood in seoul
Abstract
Purpose: There are scanty epidemiologic data on the prevalence of food allergy (FA) among preschool children in Asia. We performed this study to determine the prevalence and causative foods of immediate-type FA in early childhood in Korea.
Methods: A questionnaire-based, cross-sectional study was performed between September and October 2011. Children aged 0-6 years were recruited from 301 public child care centers in Seoul. Parents were asked to complete a questionnaire on FA. Children with FA were classified into "perceived FA, ever," "immediate-type FA, ever," and "immediate-type FA, current" according to the algorithm.
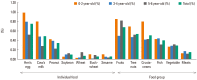
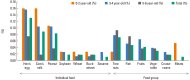
Results: A total of 16,749 children were included in this study. The prevalence of "perceived FA, ever," "immediate-type FA, ever," and "immediate-type FA, current" was 15.1%, 7.0%, and 3.7%, respectively. "Immediate-type FA, current" was reported by 182 (4.9%) out of 3,738 children aged ≤2 years, 262 (3.4%) of 7,648 children aged 3-4 years, and 177 (3.3%) of 5,363 children aged 5-6 years. Hen's egg (126/621) was the most frequent cause as the individual food item, followed by cow's milk (82/621) and peanut (58/621). Among the food groups, fruits (114/621), tree nuts (90/621) and crustaceans (85/621) were the most common offending foods. The three leading causes of food-induced anaphylaxis were hen's egg (22/47), cow's milk (15/47), and peanut (14/47).
Conclusions: The prevalence of immediate-type FA in early childhood is 3.7%, and is higher in younger children. The most common offending foods differed with age.
Keywords: Immediate hypersensitivity; child; food allergy; prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no financial or other issues that might lead to conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125:S116–S125. - PubMed
-
- Rona RJ, Keil T, Summers C, Gislason D, Zuidmeer L, Sodergren E, Sigurdardottir ST, Lindner T, Goldhahn K, Dahlstrom J, McBride D, Madsen C. The prevalence of food allergy: a meta-analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120:638–646. - PubMed
-
- Lao-araya M, Trakultivakorn M. Prevalence of food allergy among preschool children in northern Thailand. Pediatr Int. 2012;54:238–243. - PubMed
-
- Wu TC, Tsai TC, Huang CF, Chang FY, Lin CC, Huang IF, Chu CH, Lau BH, Wu L, Peng HJ, Tang RB. Prevalence of food allergy in Taiwan: a questionnaire-based survey. Intern Med J. 2012;42:1310–1315. - PubMed
-
- Ahn K, Kim J, Hahm MI, Lee SY, Kim WK, Chae Y, Park YM, Han MY, Lee KJ, Kim JK, Yang ES, Kwon HJ. Prevalence of immediate-type food allergy in Korean schoolchildren: a population-based study. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012;33:481–487. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources