Primary headache disorders at a tertiary health facility in Lagos, Nigeria: prevalence and consultation patterns
- PMID: 24587991
- PMCID: PMC3920920
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/782915
Primary headache disorders at a tertiary health facility in Lagos, Nigeria: prevalence and consultation patterns
Abstract
Background: Primary headaches are underdiagnosed and undertreated, with a significant impact on social activities and work.
Aim: To determine the last-year prevalence and health care utilization pattern of primary headaches at a tertiary centre.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was carried out amongst staff of the Lagos State University Teaching Hospital in Lagos, Nigeria. 402 staff members were selected by simple random sampling and administered a detailed structured headache assessment questionnaire. Migraine and tension-type headache were diagnosed according to the criteria of the International Headache Society (2004).
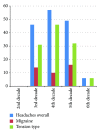
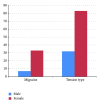
Results: The participants comprised 168 males and 234 females. The mean age was 36.9 ± 7.9 years. The overall headache prevalence was 39.3% with female predominance (P < 0.0001). Tension-type headache was the most prevalent at 72.8% and migraine at 18.9%. Unclassifiable headache constituted 8.2%. Migraine headache showed female preponderance (P = 0.000). 80.4% of participants did not seek medical consultation compared with 19.6% who did (P = 0.000). Of the latter, 83.9% consulted the general practitioner (GP), whilst 16.1% consulted the neurologist.
Conclusions: Primary headache prevalence is high in our population. It is not recognised as that requiring care by most of the staff of this tertiary health facility; thus education is required to increase health care utilization.
Figures
References
-
- Andlin-Sobocki P, Jönsson B, Wittchen H, Olesen J. Cost of disorders of the brain in Europe. European Journal of Neurology. 2005;12(1):1–27. - PubMed
-
- Edmeads J, Findlay H, Tugwell P, Pryse-Phillips W, Nelson RF, Murray TJ. Impact of migraine and tension-type headache on life-style, consulting behaviour, and medication use: a Canadian population survey. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. 1993;20(2):131–137. - PubMed
-
- Osterhaus JT, Gutterman DL, Plachetka JR. Healthcare resource and lost labour costs of migraine headache in the US. PharmacoEconomics. 1992;2(1):67–76. - PubMed
-
- Stovner LJ, Hagen K, Jensen R, et al. The global burden of headache: a documentation of headache prevalence and disability worldwide. Cephalalgia. 2007;27(3):193–210. - PubMed
-
- Stewart WF, Ricci JA, Chee E, Morganstein D, Lipton R. Lost productive time and cost due to common pain conditions in the US workforce. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2003;290(18):2443–2454. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical