Knockout mice reveal key roles for claudin 18 in alveolar barrier properties and fluid homeostasis
- PMID: 24588076
- PMCID: PMC4148039
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0353OC
Knockout mice reveal key roles for claudin 18 in alveolar barrier properties and fluid homeostasis
Abstract
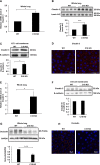
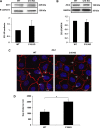
Claudin proteins are major constituents of epithelial and endothelial tight junctions (TJs) that regulate paracellular permeability to ions and solutes. Claudin 18, a member of the large claudin family, is highly expressed in lung alveolar epithelium. To elucidate the role of claudin 18 in alveolar epithelial barrier function, we generated claudin 18 knockout (C18 KO) mice. C18 KO mice exhibited increased solute permeability and alveolar fluid clearance (AFC) compared with wild-type control mice. Increased AFC in C18 KO mice was associated with increased β-adrenergic receptor signaling together with activation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, higher epithelial sodium channel, and Na-K-ATPase (Na pump) activity and increased Na-K-ATPase β1 subunit expression. Consistent with in vivo findings, C18 KO alveolar epithelial cell (AEC) monolayers exhibited lower transepithelial electrical resistance and increased solute and ion permeability with unchanged ion selectivity. Claudin 3 and claudin 4 expression was markedly increased in C18 KO mice, whereas claudin 5 expression was unchanged and occludin significantly decreased. Microarray analysis revealed changes in cytoskeleton-associated gene expression in C18 KO mice, consistent with observed F-actin cytoskeletal rearrangement in AEC monolayers. These findings demonstrate a crucial nonredundant role for claudin 18 in the regulation of alveolar epithelial TJ composition and permeability properties. Increased AFC in C18 KO mice identifies a role for claudin 18 in alveolar fluid homeostasis beyond its direct contributions to barrier properties that may, at least in part, compensate for increased permeability.
Keywords: alveolar fluid clearance; bioelectrical properties; permeability; tight junction; β2-adrenergic receptor.
Figures





References
-
- Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M. Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:285–293. - PubMed
-
- Flodby P, Borok B, Crandall ED, Kim KJ. Claudins and Barrier Function of the Lung. In: Yu ASL, editor. Claudins. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2010. pp. 177–194.
-
- Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM. Claudins and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006;68:403–429. - PubMed
-
- Chen SP, Zhou B, Willis BC, Sandoval AJ, Liebler JM, Kim KJ, Ann DK, Crandall ED, Borok Z. Effects of transdifferentiation and EGF on claudin isoform expression in alveolar epithelial cells. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2005;98:322–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10 RR022508/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL114959/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL089445/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL062569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL056590/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL108364/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089445/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES017034/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HL062569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL112638/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095349/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK048522/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL062569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL114094/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ES017034/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL108634/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL095349/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL114094/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL056590/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL114959/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

