TLR4 contributes to the host response to Klebsiella intraocular infection
- PMID: 24588082
- PMCID: PMC4144821
- DOI: 10.3109/02713683.2014.883412
TLR4 contributes to the host response to Klebsiella intraocular infection
Abstract
Purpose/aim: Klebsiella pneumoniae causes a blinding infection called endogenous endophthalmitis. The role of innate immune recognition of K. pneumoniae in the eye during infection is not known. We hypothesized that intraocular recognition of K. pneumoniae was mediated by Toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 and may be dependent on MagA-regulated hypermucoviscosity.
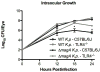
Materials and methods: Experimental endophthalmitis was induced in C57BL/6J or TLR4(-/-) mice by intravitreal injection of 100 CFU of wild type or ΔmagA K. pneumoniae. Infection and inflammation were quantified by determining viable K. pneumoniae per eye, retinal responses via electroretinography, myeloperoxidase activity of infiltrating neutrophils and the proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine response.
Results: C57BL/6J and TLR4(-/-) mice could not control intraocular wild-type K. pneumoniae growth. TLR4(-/-) mice were less able than C57BL/6J to control the intraocular growth of ΔmagA K. pneumoniae. Retinal function testing suggested that infection with ΔmagA K. pneumoniae resulted in less retinal function loss. There was a TLR4-dependent delay in initial neutrophil recruitment, regardless of the infecting organism. The proinflammatory cytokine/chemokine data supported these results. These findings were not due to an inability of TLR4(-/-) neutrophils to recognize or kill K. pneumoniae.
Conclusions: These studies suggest that TLR4 is important in the early intraocular recognition and host response to K. pneumoniae. However, the role of MagA in TLR4-mediated intraocular recognition and subsequent inflammation is less clear.
Keywords: Endophthalmitis; Klebsiella pneumoniae; Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4); eye; hypermucoviscosity.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures






Similar articles
-
TLR4 modulates inflammatory gene targets in the retina during Bacillus cereus endophthalmitis.BMC Ophthalmol. 2018 Apr 16;18(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12886-018-0764-8. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29661181 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 in experimental Bacillus cereus endophthalmitis.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028619. Epub 2011 Dec 6. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22163046 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of mucoviscosity-associated gene A (magA) to virulence in experimental Klebsiella pneumoniae endophthalmitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Aug 29;52(9):6860-6. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-7798. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21791595 Free PMC article.
-
Targets of immunomodulation in bacterial endophthalmitis.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019 Nov;73:100763. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2019.05.004. Epub 2019 May 28. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 31150824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Endogenous Klebsiella pneumoniae endophthalmitis associated with Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia: 3 cases report and literature review].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2019 Jun 12;42(6):438-443. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-0939.2019.06.007. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31189230 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Unexpected Roles for Toll-Like Receptor 4 and TRIF in Intraocular Infection with Gram-Positive Bacteria.Infect Immun. 2015 Oct;83(10):3926-36. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00502-15. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26195555 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling intraocular bacterial infections.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016 Sep;54:30-48. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 May 3. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 27154427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TLR4 modulates inflammatory gene targets in the retina during Bacillus cereus endophthalmitis.BMC Ophthalmol. 2018 Apr 16;18(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12886-018-0764-8. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29661181 Free PMC article.
-
Role of endosomal toll-like receptors in immune sensing of Klebsiella pneumoniae.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 3;16:1538425. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1538425. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40248691 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish are Resistant to Staphylococcus aureus Endophthalmitis.Pathogens. 2019 Oct 26;8(4):207. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8040207. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 31717750 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
