Localization of BDNF expression in the developing brain of zebrafish
- PMID: 24588510
- PMCID: PMC3981499
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.12168
Localization of BDNF expression in the developing brain of zebrafish
Abstract
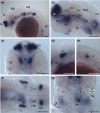
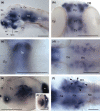
The brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene is expressed in differentiating and post-mitotic neurons of the zebrafish embryo, where it has been implicated in Huntington's disease. Little is known, however, about the full complement of neuronal cell types that express BDNF in this important vertebrate model. Here, we further explored the transcriptional profiles during the first week of development using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and whole-mount in situ hybridization (WISH). RT-qPCR results revealed a high level of maternal contribution followed by a steady increase of zygotic transcription, consistent with the notion of a prominent role of BDNF in neuronal maturation and maintenance. Based on WISH, we demonstrate for the first time that BDNF expression in the developing brain of zebrafish is structure specific. Anatomical criteria and co-staining with genetic markers (shh, pax2a, emx1, krox20, lhx2b and lhx9) visualized major topological domains of BDNF-positive cells in the pallium, hypothalamus, posterior tuberculum and optic tectum. Moreover, the relative timing of BDNF transcription in the eye and tectum may illustrate a mechanism for coordinated development of the retinotectal system. Taken together, our results are compatible with a local delivery and early role of BDNF in the developing brain of zebrafish, adding basic knowledge to the study of neurotrophin functions in neural development and disease.
Keywords: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; central nervous system; development; real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; whole-mount in situ hybridization; zebrafish.
© 2014 Anatomical Society.
Figures



Similar articles
-
BDNF, Brain, and Regeneration: Insights from Zebrafish.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 13;19(10):3155. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103155. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30322169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF Expression in Larval and Adult Zebrafish Brain: Distribution and Cell Identification.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 23;11(6):e0158057. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158057. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27336917 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and cell localization of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and TrkB during zebrafish retinal development.J Anat. 2010 Sep;217(3):214-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2010.01268.x. Epub 2010 Jul 21. J Anat. 2010. PMID: 20649707 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and TrkB tyrosine kinase receptor gene expression in zebrafish embryo and larva.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2001 Oct;19(6):569-87. doi: 10.1016/s0736-5748(01)00041-7. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11600319
-
Neuroanatomical distribution and functions of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in zebrafish (Danio rerio) brain.J Neurosci Res. 2020 May;98(5):754-763. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24536. Epub 2019 Sep 18. J Neurosci Res. 2020. PMID: 31532010 Review.
Cited by
-
BDNF, Brain, and Regeneration: Insights from Zebrafish.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 13;19(10):3155. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103155. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30322169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cluster analysis profiling of behaviors in zebrafish larvae treated with antidepressants and pesticides.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2018 Sep-Oct;69:54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2017.10.009. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2018. PMID: 29101052 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of BDNF and Calretinin in Olfactory Epithelium and Taste Buds of Zebrafish (Danio rerio).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 23;23(9):4696. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094696. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563087 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent Fasting: Potential Utility in the Treatment of Chronic Pain across the Clinical Spectrum.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 18;14(12):2536. doi: 10.3390/nu14122536. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35745266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temperature- and chemical-induced neurotoxicity in zebrafish.Front Physiol. 2023 Oct 3;14:1276941. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1276941. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37854466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson SA. Determination of cell fate within telencephalon. Chem Senses. 2002;7:573–575. - PubMed
-
- Ando H, Kobayashi M, Tsubokawa T, et al. Lhx2 mediates the activity of Six3 in zebrafish forebrain growth. Dev Biol. 2005;287:456–468. - PubMed
-
- Antal A, Chaieb L, Moliadze V, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene polymorphisms shape cortical plasticity in humans. Brain Stimul. 2010;3:230–237. - PubMed
-
- Arancio O, Chao MV. Neurotrophins, synaptic plasticity and dementia. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007;17:325–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

