Orthostatic hypotension associated with baroreceptor dysfunction: treatment approaches
- PMID: 24588814
- PMCID: PMC8031868
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.12258
Orthostatic hypotension associated with baroreceptor dysfunction: treatment approaches
Abstract
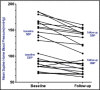
Orthostatic hypotension (OH) is a relatively common heterogeneous and multifactorial disorder often caused by autonomic dysfunction. This condition has a deleterious impact on quality of life and contributes to higher mortality rates. Supine hypertension is very common in patients with autonomic failure, limits the use of pressor agents, and can result in end-organ damage. Current recommendations on the optimal management of these patients are based on expert opinion and poor-quality small cross-sectional studies including patients with primary autonomic failure and severe orthostatic hypotension. The authors present their treatment approach in 12 patients with disabling orthostatic hypotension and supine hypertension not related to primary autonomic failure, presenting to a referral center over a 4-year period. The first step is to educate the patient about the pathophysiology and course of their disorder. Nonpharmacologic therapies and maneuvers are usually effective in relieving symptoms and preventing syncope. If needed, pharmacologic options such as fludrocortisones and midodrine are also available in patients with severe symptoms. Supine hypertension represents a challenge in the treatment of this condition. Therefore, elevation of the bed of the head and dosing of short-acting antihypertensive agents at bedtime is often indicated.
©2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Gupta V, Lipsitz LA. Orthostatic hypotension in the elderly: diagnosis and treatment. Am J Med. 2007;120:841–847. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro MH, Ruiz‐Ramon P, Fainman C, Ziegler MG. Light‐headedness and defective cardiovascular reflexes after neck radiotherapy. Blood Press Monit. 1996;1:81–85. - PubMed
-
- Freeman R, Wieling W, Axelrod FB, et al. Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, neurally mediated syncope and the postural tachycardia syndrome. Auton Neurosci. 2011;161:46–48. - PubMed
-
- Shannon J, Jordan J, Costa F, et al. The hypertension of autonomic failure and its treatment. Hypertension. 1997;30:1062–1067. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

