Autosomal recessive phosphoglucomutase 3 (PGM3) mutations link glycosylation defects to atopy, immune deficiency, autoimmunity, and neurocognitive impairment
- PMID: 24589341
- PMCID: PMC4016982
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.02.013
Autosomal recessive phosphoglucomutase 3 (PGM3) mutations link glycosylation defects to atopy, immune deficiency, autoimmunity, and neurocognitive impairment
Abstract
Background: Identifying genetic syndromes that lead to significant atopic disease can open new pathways for investigation and intervention in allergy.
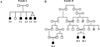
Objective: We sought to define a genetic syndrome of severe atopy, increased serum IgE levels, immune deficiency, autoimmunity, and motor and neurocognitive impairment.
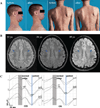
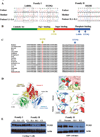
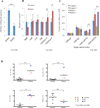
Methods: Eight patients from 2 families with similar syndromic features were studied. Thorough clinical evaluations, including brain magnetic resonance imaging and sensory evoked potentials, were performed. Peripheral lymphocyte flow cytometry, antibody responses, and T-cell cytokine production were measured. Whole-exome sequencing was performed to identify disease-causing mutations. Immunoblotting, quantitative RT-PCR, enzymatic assays, nucleotide sugar, and sugar phosphate analyses, along with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry of glycans, were used to determine the molecular consequences of the mutations.
Results: Marked atopy and autoimmunity were associated with increased T(H)2 and T(H)17 cytokine production by CD4(+) T cells. Bacterial and viral infection susceptibility were noted along with T-cell lymphopenia, particularly of CD8(+) T cells, and reduced memory B-cell numbers. Apparent brain hypomyelination resulted in markedly delayed evoked potentials and likely contributed to neurologic abnormalities. Disease segregated with novel autosomal recessive mutations in a single gene, phosphoglucomutase 3 (PGM3). Although PGM3 protein expression was variably diminished, impaired function was demonstrated by decreased enzyme activity and reduced uridine diphosphate-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, along with decreased O- and N-linked protein glycosylation in patients' cells. These results define a new congenital disorder of glycosylation.
Conclusions: Autosomal recessive hypomorphic PGM3 mutations underlie a disorder of severe atopy, immune deficiency, autoimmunity, intellectual disability, and hypomyelination.
Keywords: Atopy; allergy; autoimmunity; glycosylation; hyper-IgE; immune deficiency; neurocognitive impairment; phosphoglucomutase 3.
Published by Mosby, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Davis SD, Schaller J, Wedgwood RJ. Job's Syndrome. Recurrent, "cold", staphylococcal abscesses. Lancet. 1966;1:1013–1015. - PubMed
-
- Buckley RH, Wray BB, Belmaker EZ. Extreme hyperimmunoglobulinemia E and undue susceptibility to infection. Pediatrics. 1972;49:59–70. - PubMed
-
- Holland SM, DeLeo FR, Elloumi HZ, Hsu AP, Uzel G, Brodsky N, et al. STAT3 mutations in the hyper-IgE syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1608–1619. - PubMed
-
- Minegishi Y, Saito M, Tsuchiya S, Tsuge I, Takada H, Hara T, et al. Dominant- negative mutations in the DNA-binding domain of STAT3 cause hyper-IgE syndrome. Nature. 2007;448:1058–1062. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

