Unsupervised phenotyping of Severe Asthma Research Program participants using expanded lung data
- PMID: 24589344
- PMCID: PMC4038417
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.11.042
Unsupervised phenotyping of Severe Asthma Research Program participants using expanded lung data
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have identified asthma phenotypes based on small numbers of clinical, physiologic, or inflammatory characteristics. However, no studies have used a wide range of variables using machine learning approaches.
Objectives: We sought to identify subphenotypes of asthma by using blood, bronchoscopic, exhaled nitric oxide, and clinical data from the Severe Asthma Research Program with unsupervised clustering and then characterize them by using supervised learning approaches.
Methods: Unsupervised clustering approaches were applied to 112 clinical, physiologic, and inflammatory variables from 378 subjects. Variable selection and supervised learning techniques were used to select relevant and nonredundant variables and address their predictive values, as well as the predictive value of the full variable set.
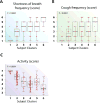
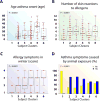
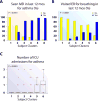
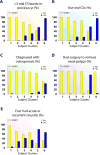
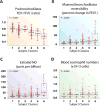
Results: Ten variable clusters and 6 subject clusters were identified, which differed and overlapped with previous clusters. Patients with traditionally defined severe asthma were distributed through subject clusters 3 to 6. Cluster 4 identified patients with early-onset allergic asthma with low lung function and eosinophilic inflammation. Patients with later-onset, mostly severe asthma with nasal polyps and eosinophilia characterized cluster 5. Cluster 6 asthmatic patients manifested persistent inflammation in blood and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and exacerbations despite high systemic corticosteroid use and side effects. Age of asthma onset, quality of life, symptoms, medications, and health care use were some of the 51 nonredundant variables distinguishing subject clusters. These 51 variables classified test cases with 88% accuracy compared with 93% accuracy with all 112 variables.
Conclusion: The unsupervised machine learning approaches used here provide unique insights into disease, confirming other approaches while revealing novel additional phenotypes.
Keywords: Asthma phenotyping; supervised machine learning approaches; unsupervised approaches; variable analysis.
Copyright © 2014 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Wenzel SE. Asthma phenotypes: the evolution from clinical to molecular approaches. Nat Med. 2012;18:716–25. - PubMed
-
- Siroux V, Garcia-Aymerich J. The investigation of asthma phenotypes. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;11:393–9. - PubMed
-
- Fitzpatrick AM, Teague WG, Meyers DA, Peters SP, Li X, Li H, et al. Heterogeneity of severe asthma in childhood: confirmation by cluster analysis of children in the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Severe Asthma Research Program. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127:382–9. e1–13. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL69174/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069116/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL69349/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069349/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DA035778/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM087694/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069130/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR03186/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL087665/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109257/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069155/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL69170/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL69149/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000427/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HL69116/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087665/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069174/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR003186/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069149/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069170/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL69167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL69155/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR07122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR018390/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL69174/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM087694/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR007122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL69130/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109172/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

