Bacterial degradation of chlorophenols and their derivatives
- PMID: 24589366
- PMCID: PMC3975901
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-13-31
Bacterial degradation of chlorophenols and their derivatives
Abstract
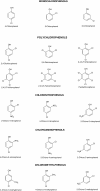
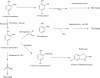
Chlorophenols (CPs) and their derivatives are persistent environmental pollutants which are used in the manufacture of dyes, drugs, pesticides and other industrial products. CPs, which include monochlorophenols, polychlorophenols, chloronitrophenols, chloroaminophenols and chloromethylphenols, are highly toxic to living beings due to their carcinogenic, mutagenic and cytotoxic properties. Several physico-chemical and biological methods have been used for removal of CPs from the environment. Bacterial degradation has been considered a cost-effective and eco-friendly method of removing CPs from the environment. Several bacteria that use CPs as their sole carbon and energy sources have been isolated and characterized. Additionally, the metabolic pathways for degradation of CPs have been studied in bacteria and the genes and enzymes involved in the degradation of various CPs have been identified and characterized. This review describes the biochemical and genetic basis of the degradation of CPs and their derivatives.
Figures









References
-
- National Pollutant Inventory. Department of the environment, water, heritage and the arts, Australia. [ http://www.npi.gov.au/resource/chlorophenols-di-tri-tetra]
-
- Muller F, Caillard L. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2011. Chlorophenols. DOI: 10.1002/14356007.a07_001.pub2.
-
- Olaniran AO, Igbinosa EO. Chlorophenols and other related derivatives of environmental concern: properties, distribution and microbial degradation processes. Chemosphere. 2011;83:1297–1306. - PubMed
-
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) Toxicological Profile for Chlorophenols. Atlanta, GA: U.S Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service; 1999.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

