Bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation promotes therapeutic angiogenesis via upregulation of the VEGF-VEGFR2 signaling pathway in a rat model of vascular dementia
- PMID: 24589546
- PMCID: PMC4000455
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.02.033
Bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation promotes therapeutic angiogenesis via upregulation of the VEGF-VEGFR2 signaling pathway in a rat model of vascular dementia
Abstract
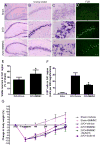
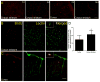
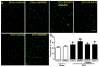
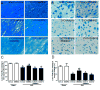
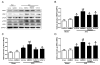
Bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMNCs) are important for angiogenesis after stroke. We investigated the effects of BMMNCs on cognitive function, angiogenesis, and the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2) signaling pathway in a rat model of vascular dementia. We transplanted BMMNCs into rats that had undergone permanent bilateral occlusion of the common carotid arteries (2VO) and observed their migration in vivo. On day 28, we assessed cognitive function with the Morris Water Maze test and examined vascular density and white matter damage within the corpus striatum by staining with fluorescein lycopersicon esculentum (tomato) lectin or Luxol fast blue. We evaluated expression of VEGF, rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma 1 (Raf1), and extracellular-signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) in the ischemic hemisphere by Western blot analysis on day 7 after cell transplantation. Contribution of the VEGF-VEGFR2 signaling pathway was confirmed by using VEGFR2 inhibitor SU5416. BMMNCs penetrated the blood-brain barrier and reached the ischemic cortex and white matter or incorporated into vascular walls of 2VO rats. BMMNC-treated 2VO rats had better learning and memory, higher vascular density, and less white matter damage than did vehicle-treated rats. The beneficial effects of BMMNCs were abolished by pretreatment of rats with SU5416. Protein expression of VEGF and phosphorylated Raf1 and ERK1/2 was also significantly increased by BMMNC treatment, but this upregulation was reversed by SU5416. BMMNCs can enhance angiogenesis, reduce white matter damage, and promote cognitive recovery in 2VO rats. The angiogenic effect may result from upregulation of the VEGF-VEGFR2 signaling pathway.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Bone marrow mononuclear cells; Cell transplantation; VEGF–VEGFR2 signaling pathway; Vascular dementia.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preconditioning with VEGF Enhances Angiogenic and Neuroprotective Effects of Bone Marrow Mononuclear Cell Transplantation in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Nov;53(9):6057-6068. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9512-8. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26530694 Free PMC article.
-
Erythropoietin improves hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonatal rats after short-term anoxia by enhancing angiogenesis.Brain Res. 2016 Nov 15;1651:104-113. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.09.024. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27659964
-
Electroacupuncture ameliorates cognitive impairment and white matter injury in vascular dementia rats via activating HIF-1α/VEGF/VEGFR2 pathway.Neuroscience. 2025 May 7;573:364-380. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2025.03.063. Epub 2025 Mar 29. Neuroscience. 2025. PMID: 40164280
-
Differential roles of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 and receptor-2 in angiogenesis.J Biochem Mol Biol. 2006 Sep 30;39(5):469-78. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2006.39.5.469. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 17002866 Review.
-
The role of VEGF in vascular dementia: impact of aging and cellular senescence.Biogerontology. 2025 Mar 22;26(2):77. doi: 10.1007/s10522-025-10219-w. Biogerontology. 2025. PMID: 40119956 Review.
Cited by
-
Transplanting Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Treatment of Ischemic Stroke.Cell Transplant. 2018 Dec;27(12):1825-1834. doi: 10.1177/0963689718795424. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Cell Transplant. 2018. PMID: 30251564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preconditioning with VEGF Enhances Angiogenic and Neuroprotective Effects of Bone Marrow Mononuclear Cell Transplantation in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Nov;53(9):6057-6068. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9512-8. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26530694 Free PMC article.
-
Possible mechanisms of lycopene amelioration of learning and memory impairment in rats with vascular dementia.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Feb;15(2):332-341. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.265565. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31552907 Free PMC article.
-
FTY720 Prevents Spatial Memory Impairment in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion via a SIRT3-Independent Pathway.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Jan 14;12:593364. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.593364. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33519419 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and Network Pharmacology to Explore the Potential Mechanisms of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. in the Treatment of Blood Stasis Syndrome.Molecules. 2024 Jun 26;29(13):3019. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133019. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38998977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan KY, Wang W, Wu JJ, et al. Epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia in China, 1990–2010: a systematic review and analysis[J] Lancet. 2013;381(9882):2016–2023. - PubMed
-
- Stasiak A, Mussur M, Unzeta M, et al. The central histamine level in rat model of vascular dementia[J] J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011;62(5):549–558. - PubMed
-
- Lindvall O, Kokaia Z, Martinez-Serrano A. Stem cell therapy for human neurodegenerative disorders--how to make it work[J] 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

