Recombinant disintegrin targets α(v) β(3) integrin and leads to mediator production
- PMID: 24589623
- PMCID: PMC3974796
- DOI: 10.4161/cam.27698
Recombinant disintegrin targets α(v) β(3) integrin and leads to mediator production
Abstract
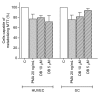
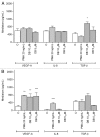
Integrin αvβ3 is most likely the foremost modulator of angiogenesis among all known integrins. Recombinant disintegrin DisBa-01, originally obtained from snake venom glands, binds to αvβ3, thereby significantly inhibiting adhesion and generating in vivo anti-metastatic ability. However, its function in mediator production is not clear. Here, we observed that the mediators VEGF-A, IL-8, and TGF-β are not produced by human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC cell line) or monocyte/macrophage cells (SC cell line) when cells adhered to vitronectin. However, when exposed to DisBa-01, HUVECs produced higher levels of TGF-β, and SC cells produced higher levels of VEGF-A. Nonetheless, HUVECs also showed an enhancement of apoptosis after losing adherence when exposed to disintegrin, which is a characteristic of anoikis. We propose that disintegrin DisBa-01 could be used to modulate integrin αvβ3 functions.
Keywords: DisBa; HUVEC; IL-8; TGF; VEGF; cancer; endothelial cell; integrin αvβ3; macrophage.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recombinant RGD-disintegrin DisBa-01 blocks integrin αvβ3 and impairs VEGF signaling in endothelial cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Mar 20;17(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0339-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 30894182 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking αvβ3 integrin by a recombinant RGD disintegrin impairs VEGF signaling in endothelial cells.Biochimie. 2012 Aug;94(8):1812-20. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2012.04.020. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Biochimie. 2012. PMID: 22561350
-
The Effects of αvβ3 Integrin Blockage in Breast Tumor and Endothelial Cells under Hypoxia In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 3;23(3):1745. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031745. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163668 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical studies of a novel snake venom-derived recombinant disintegrin with antitumor activity: A review.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Nov;181:114149. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114149. Epub 2020 Jul 12. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32663453 Review.
-
Alternagin-C, a disintegrin-like protein from the venom of Bothrops alternatus, modulates alpha2beta1 integrin-mediated cell adhesion, migration and proliferation.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2005 Oct;38(10):1505-11. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2005001000007. Epub 2005 Sep 6. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2005. PMID: 16172743 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional characterization of six aspartate (D) recombinant mojastin mutants (r-Moj): A second aspartate amino acid carboxyl to the RGD in r-Moj-D_ peptides is not sufficient to induce apoptosis of SK-Mel-28 cells.Toxicon. 2016 Aug;118:36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.04.038. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Toxicon. 2016. PMID: 27105671 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant and Chimeric Disintegrins in Preclinical Research.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Aug 7;10(8):321. doi: 10.3390/toxins10080321. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30087285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional analysis of four single (RGDWL, RGDWM, RGDWP, RGDMN) and two double (RGDNM, RGDMP) mutants: The importance of methionine (M) in the functional potency of recombinant mojastin (r-Moj).Toxicon. 2016 Dec 15;124:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.11.002. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Toxicon. 2016. PMID: 27816535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ramos OHP, Kauskot A, Cominetti MR, Bechyne I, Salla Pontes CL, Chareyre F, Manent J, Vassy R, Giovannini M, Legrand C, et al. A novel α(v)β (3)-blocking disintegrin containing the RGD motive, DisBa-01, inhibits bFGF-induced angiogenesis and melanoma metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2008;25:53–64. doi: 10.1007/s10585-007-9101-y. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
