A temporal requirement for Hippo signaling in mammary gland differentiation, growth, and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 24589775
- PMCID: PMC3950341
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.233676.113
A temporal requirement for Hippo signaling in mammary gland differentiation, growth, and tumorigenesis
Abstract
Despite recent progress, the physiological role of Hippo signaling in mammary gland development and tumorigenesis remains poorly understood. Here we show that the Hippo pathway is functionally dispensable in virgin mammary glands but specifically required during pregnancy. In contrast to many other tissues, hyperactivation of YAP in mammary epithelia does not induce hyperplasia but leads to defects in terminal differentiation. Interestingly, loss of YAP causes no obvious defects in virgin mammary glands but potently suppresses oncogene-induced mammary tumors. The selective requirement for YAP in oncogenic growth highlights the potential of YAP inhibitors as molecular targeted therapies against breast cancers.
Keywords: Hippo signaling; YAP; differentiation; mammary gland; proliferation; tumorigenesis.
Figures
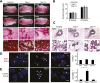
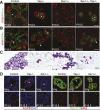
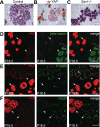
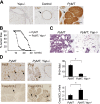
References
-
- Brisken C, Rajaram RD 2006. Alveolar and lactogenic differentiation. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 11: 239–248 - PubMed
-
- Chan SW, Lim CJ, Guo K, Ng CP, Lee I, Hunziker W, Zeng Q, Hong W 2008. A role for TAZ in migration, invasion, and tumorigenesis of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 68: 2592–2598 - PubMed
-
- Cordenonsi M, Zanconato F, Azzolin L, Forcato M, Rosato A, Frasson C, Inui M, Montagner M, Parenti AR, Poletti A, et al. 2011. The hippo transducer TAZ confers cancer stem cell-related traits on breast cancer cells. Cell 147: 759–772 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
