Twist1-induced dissemination preserves epithelial identity and requires E-cadherin
- PMID: 24590176
- PMCID: PMC3941052
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201306088
Twist1-induced dissemination preserves epithelial identity and requires E-cadherin
Abstract
Dissemination of epithelial cells is a critical step in metastatic spread. Molecular models of dissemination focus on loss of E-cadherin or repression of cell adhesion through an epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT). We sought to define the minimum molecular events necessary to induce dissemination of cells out of primary murine mammary epithelium. Deletion of E-cadherin disrupted epithelial architecture and morphogenesis but only rarely resulted in dissemination. In contrast, expression of the EMT transcription factor Twist1 induced rapid dissemination of cytokeratin-positive epithelial cells. Twist1 induced dramatic transcriptional changes in extracellular compartment and cell-matrix adhesion genes but not in cell-cell adhesion genes. Surprisingly, we observed disseminating cells with membrane-localized E-cadherin and β-catenin, and E-cadherin knockdown strongly inhibited Twist1-induced single cell dissemination. Dissemination can therefore occur with retention of epithelial cell identity. The spread of cancer cells during metastasis could similarly involve activation of an epithelial motility program without requiring a transition from epithelial to mesenchymal character.
Figures

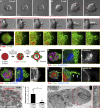

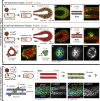




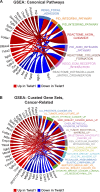
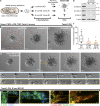
References
-
- Abramoff M.D., Magalhaes P.J., Ram S.J. 2004. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics International. 11:36–42
-
- Anders S. 2010. HTSeq: Analysing high-throughput sequencing data with Python. Available at http://www-huber.embl.de/users/anders/HTSeq/doc/index.html (Accessed on December 26, 2012) - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

