Randomized trial of bendamustine-rituximab or R-CHOP/R-CVP in first-line treatment of indolent NHL or MCL: the BRIGHT study
- PMID: 24591201
- PMCID: PMC4260975
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-11-531327
Randomized trial of bendamustine-rituximab or R-CHOP/R-CVP in first-line treatment of indolent NHL or MCL: the BRIGHT study
Abstract
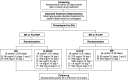
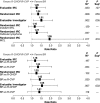
This randomized, noninferiority (NI), global, phase 3 study evaluated the efficacy and safety of bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) vs a standard rituximab-chemotherapy regimen (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone [R-CHOP] or rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone [R-CVP]) for treatment-naive patients with indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphoma or mantle cell lymphoma. Investigators preassigned the standard treatment regimen they considered most appropriate for each patient; patients were randomized to receive BR (n = 224) or standard therapy (R-CHOP/R-CVP, n = 223) for 6 cycles; 2 additional cycles were permitted at investigator discretion. Response was assessed by a blinded independent review committee. BR was noninferior to R-CHOP/R-CVP, as assessed by the primary end point of complete response rate (31% vs 25%, respectively; P = .0225 for NI [0.88 margin]). The overall response rates for BR and R-CHOP/R-CVP were 97% and 91%, respectively (P = .0102). Incidences of vomiting and drug-hypersensitivity reactions were significantly higher in patients treated with BR (P < .05), and incidences of peripheral neuropathy/paresthesia and alopecia were significantly higher in patients treated with standard-therapy regimens (P < .05). These data indicate BR is noninferior to standard therapy with regard to clinical response with an acceptable safety profile. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT00877006.
Figures

Comment in
-
Indolent and mantle cell NHL: the future is BRIGHT.Blood. 2014 May 8;123(19):2905-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-03-562124. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24810622 No abstract available.
-
Bendamustine plus rituximab: is it a BRIGHT idea?Chin Clin Oncol. 2020 Apr;9(2):22. doi: 10.21037/cco.2019.10.03. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Chin Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31735051 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hiddemann W, Kneba M, Dreyling M, et al. Frontline therapy with rituximab added to the combination of cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) significantly improves the outcome for patients with advanced-stage follicular lymphoma compared with therapy with CHOP alone: results of a prospective randomized study of the German Low-Grade Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 2005;106(12):3725–3732. - PubMed
-
- Marcus R, Imrie K, Belch A, et al. CVP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CVP as first-line treatment for advanced follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2005;105(4):1417–1423. - PubMed
-
- Knauf WU, Lissichkov T, Aldaoud A, et al. Phase III randomized study of bendamustine compared with chlorambucil in previously untreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(26):4378–4384. - PubMed
-
- Robinson KS, Williams ME, van der Jagt RH, et al. Phase II multicenter study of bendamustine plus rituximab in patients with relapsed indolent B-cell and mantle cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(27):4473–4479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

