Function and regulation of the endosomal fusion and fission machineries
- PMID: 24591520
- PMCID: PMC3949357
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016832
Function and regulation of the endosomal fusion and fission machineries
Abstract
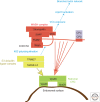
Organelles within the endomembrane system are connected via vesicle flux. Along the endocytic pathway, endosomes are among the most versatile organelles. They sort cargo through tubular protrusions for recycling or through intraluminal vesicles for degradation. Sorting involves numerous machineries, which mediate fission of endosomal transport intermediates and fusion with other endosomes or eventually with lysosomes. Here we review the recent advances in our understanding of these processes with a particular focus on the Rab GTPases, tethering factors, and retromer. The cytoskeleton has also been recently recognized as a central player in membrane dynamics of endosomes, and this review covers the regulation of the machineries that govern the formation of branched actin networks through the WASH and Arp2/3 complexes in relation with cargo recycling and endosomal fission.
Figures



References
-
- Balderhaar HJK, Arlt H, Ostrowicz CW, Bröcker C, Sündermann F, Brandt R, Babst M, Ungermann C 2010. The Rab GTPase Ypt7 is linked to retromer-mediated receptor recycling and fusion at the yeast late endosome. J Cell Sci 123: 4085–4094 - PubMed
-
- Bananis E, Murray JW, Stockert RJ, Satir P, Wolkoff AW 2003. Regulation of early endocytic vesicle motility and fission in a reconstituted system. J Cell Sci 116: 2749–2761 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
