Hepatoprotective and Antioxidant Activity of Dunaliella salina in Paracetamol-induced Acute Toxicity in Rats
- PMID: 24591738
- PMCID: PMC3928727
Hepatoprotective and Antioxidant Activity of Dunaliella salina in Paracetamol-induced Acute Toxicity in Rats
Abstract
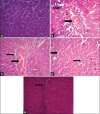
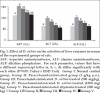
Paracetamol has a reasonable safety profile when taken in therapeutic doses. However, it could induce hepatotoxicity and even more severe fatal acute hepatic damage when taken in an overdose. The green alga, Dunaliella salina was investigated for hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity against paracetamol-induced liver damage in rats. Male albino Wistar rats overdosed with paracetamol showed liver damage and oxidative stress as indicated by significantly (P<0.05) increased serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, total and direct bilirubin, malondialdehyde, cholesterol and nitric oxide. At the same time, there were decreased activities of serum superoxide dismutase and total antioxidant capacity compared with the control group. Treatment with D. salina methanol extract at doses of 500 and 1000 mg/kg body weight or silymarin could significantly (P<0.05) decrease the liver damage marker enzymes, total and direct bilirubin, malondialdehyde, cholesterol and nitric oxide levels and increase the activities of superoxide dismutase and total antioxidant capacity in serum when compared with paracetamol intoxicated group. Liver histopathology also showed that D. salina reduced the centrilobular necrosis, congestion and inflammatory cell infiltration evoked by paracetamol overdose. These results suggest that D. salina exhibits a potent hepatoprotective effect on paracetamol-induced liver damage in rats, which may be due to both the increase of antioxidant enzymes activity and inhibition of lipid peroxidation.
Keywords: Dunaliella salina; antioxidant; hepatotoxicity; paracetamol; reactive oxygen species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effects of Dunaliella salina--a carotenoids-rich alga, against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Oct;46(10):3311-7. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.07.027. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18761048
-
The Protective Action of the Aqueous Extract of Auricularia polytricha in Paracetamol Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2016;10(1):72-6. doi: 10.2174/1872211309666151030110015. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2016. PMID: 26517821
-
Profile of bioactive compounds in Nymphaea alba L. leaves growing in Egypt: hepatoprotective, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jan 17;17(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1561-2. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28095910 Free PMC article.
-
Potential protective effect of honey against paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity.Arch Iran Med. 2012 Nov;15(11):674-80. Arch Iran Med. 2012. PMID: 23102243
-
[The role of oxidative/nitrosative stress in pathogenesis of paracetamol-induced toxic hepatitis].Med Pregl. 2010 Nov-Dec;63(11-12):827-32. doi: 10.2298/mpns1012827r. Med Pregl. 2010. PMID: 21553462 Review. Serbian.
Cited by
-
Protective Effects of Diallyl Sulfide and Curcumin Separately against Thallium-Induced Toxicity in Rats.Cell J. 2015 Summer;17(2):379-88. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2016.3752. Epub 2015 Jul 11. Cell J. 2015. PMID: 26199917 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating Effects of Spirulina platensis against Tilmicosin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Mice.Cell J. 2015 Spring;17(1):137-44. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2015.520. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Cell J. 2015. PMID: 25870843 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic protective role of ceftriaxone and ascorbic acid against subacute diazinon-induced nephrotoxicity in rats.Cytotechnology. 2016 Mar;68(2):279-89. doi: 10.1007/s10616-014-9779-z. Epub 2014 Aug 24. Cytotechnology. 2016. PMID: 25150555 Free PMC article.
-
Dunaliella salina Attenuates Diabetic Neuropathy Induced by STZ in Rats: Involvement of Thioredoxin.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jan 2;2020:1295492. doi: 10.1155/2020/1295492. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31998774 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary supplementation with Dunaliella salina microalga promotes quail growth by altering lipid profile and immunity.Poult Sci. 2024 May;103(5):103591. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103591. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 38471224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shariati M, Lilley RM. Loss of intracellular glycerol from Dunaliella by electroporation at constant osmotic pressure: Subsequent restoration of glycerol content and associated volume changes. Plant Cell Environ. 1994;17:1295–304.
-
- Avron M, Ben-Amotz A. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 1992. Dunaliella: Physiology, biochemistry, and biotechnology; p. 240.
-
- Shariati M, Hadi M. Isolation, purification and identification of three unicellular green alga species of Dunaliella salina, Dunaliella parva and Dunaliella pseudosalina from salt marsh of Gave-Khoni of Isfahan-Iran. Iran J Biol. 2000;9:45–54.
-
- Phadwal K, Singh PK. Isolation and characterization of an indigenous isolate of Dunaliella sp. for β-carotene and glycerol production from a hypersaline lake in India. J Basic Microbiol. 2003;43:423–29. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
