Joubert syndrome and related disorders, prenatal diagnosis with ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 24592023
- PMCID: PMC3939136
- DOI: 10.5152/jtgga.2011.75
Joubert syndrome and related disorders, prenatal diagnosis with ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
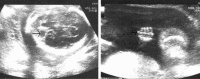
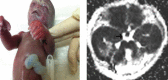
Joubert syndrome (JBTS) is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by intellectual disability, hypotonia, ataxia, tachypnea/apnea, and abnormal eye movements. A pathognomonic midbrain-hindbrain malformation seen on cranial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which consists of hypoplasia of the midline cerebellar vermis that resembles the cross-section through a molar tooth, has been described previously. The molar tooth sign is defined by a peculiar appearance resembling a molar tooth secondary to an abnormally deep interpeduncular fossa and enlarged superior cerebellar peduncles on axial images at the pontomesencephalic level. The term Joubert Syndrome and Related Disorders (JSRD) has recently been adopted to describe all disorders presenting the "molar tooth sign" (MTS) on brain imaging. JSRD is characterized by lack of decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncles, central pontine tracts and corticospinal tracts suggesting defective axon guidance. Prenatal sonographic findings in fetuses with JSRD are relatively nonspecific and include increased nuchal translucency, enlarged cisterna magna, cerebellar vermian agenesis, occipital encephalocele, ventriculomegaly and polydactyly. We report a case of JSRD detected prenatally at 23 weeks of gestation. The fetus in the present case had a normal karyotype. Sonographic features of the fetus included polydactyly, partial vermian hypoplasia, dilated 4(th) ventricle and mild ventriculomegaly which were also confirmed by prenatal MRI. MTS was demonstrated in a postnatal MRI after pregnancy termination.
Joubert sendromu entellektüel bozukluk, hipotoni, ataksi, takipne/apne ve anormal göz hareketleri ile karakterize otozomal resesif bir hastalıktır. Önceki çalışmalarda kraniyal manyetik rezonans görüntüleme ile hastalığa ait patognomonik bir görüntü saptanmıştır. Bu görüntü molar diş görünümü olarak ifade edilmiştir. Molar diş görüntüsü anormal derin yerleşimli interpedünküler fossa ve genişlemiş superior serebellar pedünkülllere bağlı olarak pontomezensefalik seviyedeki aksial kesitlerde ortaya çıkmaktadır. Joubert sendromu ve ilişkili bozukluklar son dönemde molar diş görünümünün olduğu tüm bozukluklar için kullanılmaktadır. Joubert sendromu ve ilişkili bozukluklar, superior serebellar pedünküllerde, santral pontin yollarda ve kortikospinal yollarda çaprazlaşmanın olmaması ile karakterize bir grup hastalıktır. Bu hastalığa ait prenatal sonografik bulgular görece non spesifiktir. Başlıca bulgular arasında artmış nukal saydamlık, genişlemiş sisterna magna, serebellar vermian agenezi oksipital ensefalosel ve polidaktili vardır. Biz, 23. haftada sonografik olarak polidaktili, vermian agenezi, dilate 4. ventrikül ve hafif ventrikülomegali saptanan normal karyotipli bir Joubert sendromu olgusu sunmaktayız. Bu olguda molar diş işareti doğum sonrası manyetik rezonans görüntüleme ile saptanmıştır.
Keywords: Joubert syndrome; cerebellar vermian agenenesis; polydactyly; prenatal diagnosis; ultrasonography.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of MR imaging in prenatal diagnosis of pregnancies at risk for Joubert syndrome and related cerebellar disorders.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010 Mar;31(3):424-9. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1867. Epub 2009 Nov 26. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010. PMID: 19942698 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prenatal magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis of molar tooth sign at 17 to 18 weeks of gestation in two fetuses at risk for Joubert syndrome and related cerebellar disorders.Neuropediatrics. 2011 Feb;42(1):35-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1275739. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Neuropediatrics. 2011. PMID: 21500139
-
Joubert syndrome: the molar tooth sign of the mid-brain.Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2013 Apr;3(2):291-4. doi: 10.4103/2141-9248.113686. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2013. PMID: 23919210 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical nosologic and genetic aspects of Joubert and related syndromes.J Child Neurol. 1999 Oct;14(10):660-6; discussion 669-72. doi: 10.1177/088307389901401007. J Child Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10511339 Review.
-
Clinical and molecular features of Joubert syndrome and related disorders.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2009 Nov 15;151C(4):326-40. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.30229. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2009. PMID: 19876931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis of Joubert syndrome via ultrasonography.J Med Ultrason (2001). 2017 Apr;44(2):197-202. doi: 10.1007/s10396-016-0751-8. Epub 2016 Oct 26. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2017. PMID: 27785575
-
Primary Cilia Signaling Promotes Axonal Tract Development and Is Disrupted in Joubert Syndrome-Related Disorders Models.Dev Cell. 2019 Dec 16;51(6):759-774.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.11.005. Dev Cell. 2019. PMID: 31846650 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal diagnosis of Joubert syndrome: A case report.Radiol Case Rep. 2024 Jul 29;19(10):4369-4374. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2024.07.009. eCollection 2024 Oct. Radiol Case Rep. 2024. Retraction in: Radiol Case Rep. 2025 Apr 11;20(6):3159. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2024.12.027. PMID: 39165313 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Diagnostic Value of Prenatal MR Imaging in the Detection of Brain Malformations in Fetuses before the 26th Week of Gestational Age.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016 May;37(5):946-51. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4639. Epub 2015 Dec 31. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016. PMID: 26721771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- D’Angelo A, Franco B. The primary cilium in different tissues-lessons from patients and animal models. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011;26:655–62. - PubMed
-
- Joubert M, Eisenring JJ, Andermann F. Familial dysgenesis of the vermis, a syndrome of hyperventilation, abnormal eye movements and retardation. Neurology. 1968;18:302–3. - PubMed
-
- Yachnis AT, Rorke LB. Neuropathology of Joubert syndrome. J ChildNeurol. 1999;14:655–9. - PubMed
-
- Maria BL, Hoang KB, Tusa RJ, Mancuso AA, Hamed LM, Quisling RG, et al. “Joubert syndrome” revisited, key ocular motor signs with magnetic resonance imaging correlation, J”. Child Neurol. 1997;12:423–30. - PubMed
-
- Badano JL, Mitsuma N, Beales PL, Katsanis N. The Ciliopathies, An Emerging Class of Human Genetic Disorders. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2006;7:125–48. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
