Streptomyces infection in Cushing syndrome: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 24592373
- PMCID: PMC3928849
- DOI: 10.4103/2277-9175.124672
Streptomyces infection in Cushing syndrome: A case report and literature review
Abstract
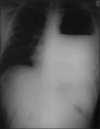
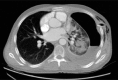
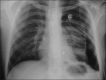
Streptomyces are saprophytic soil organisms rarely known to cause invasive infections. Streptomyces is the largest genus, producing antibacterial, antifungal and antiparasitic drugs. The case was a 24-year-old man, admitted for sudden dyspnea, fever and sputum and decreased sound in the left lung. The chest X-ray showed hydropneumothorax. After chest tube insertion, lung expansion did not happen. Pleural effusion was exudative with gram-positive bacillus and Streptomyces in culture. Owing to symptoms of Cushing in history, examination and laboratory work-up for Cushing was done and finally he underwent bilateral adrenalectomy. The patient was on antibiotic broad spectrum antibiotic and then was changed to antibiotic as organism was sensitive to and discharged with clarithromycin for 6 months. Streptomyces happens in immunodeficient patient. Diagnosis is based on culture and contamination was ruled out. Treatment period is longer for patients owing to slow growing nature.
Keywords: Cushing syndrome; Streptomyces; pulmonary infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kapadia M, Rolston KV, Han XY. Invasive Streptomyces infections: Six cases and literature review. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007;127:619–24. - PubMed
-
- Watve MG, Tickoo R, Jog MM, Bhole BD. How many antibiotics are produced by the genus Streptomyces? Arch Microbiol. 2001;176:386–90. - PubMed
-
- Dunne EF, Burman WJ, Wilson ML. Streptomyces pneumonia in a patient with human immunodeficiency virus infection: Case report and review of the literature on invasive streptomyces infections. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;27:93–6. - PubMed
-
- Kofteridis DP, Maraki S, Scoulica E, Tsioutis C, Maltezakis G, Gikas A. Streptomyces pneumonia in an immunocompetent patient: A case report and literature review. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007;59:459–62. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

