Targeting Staphylococcus aureus quorum sensing with nonpeptidic small molecule inhibitors
- PMID: 24592914
- PMCID: PMC4010551
- DOI: 10.1021/jm500215s
Targeting Staphylococcus aureus quorum sensing with nonpeptidic small molecule inhibitors
Abstract
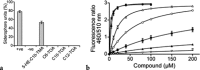
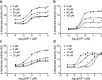
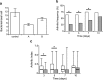
A series of 3-oxo-C12-HSL, tetramic acid, and tetronic acid analogues were synthesized to gain insights into the structural requirements for quorum sensing inhibition in Staphylococcus aureus. Compounds active against agr were noncompetitive inhibitors of the autoinducing peptide (AIP) activated AgrC receptor, by altering the activation efficacy of the cognate AIP-1. They appeared to act as negative allosteric modulators and are exemplified by 3-tetradecanoyltetronic acid 17, which reduced nasal cell colonization and arthritis in a murine infection model.
Figures
References
-
- Williams P.; Cámara M. Quorum sensing and environmental adaptation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a tale of regulatory networks and multifunctional signal molecules. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 182–191. - PubMed
-
- Kravchenko V. V.; Kaufmann G. F.; Mathison J. C.; Scott D. A.; Katz A. Z.; Grauer D. C.; Lehmann M.; Meijler M. M.; Janda K. D.; Ulevitch R. J. Modulation of gene expression via disruption of NF-kappaB signaling by a bacterial small molecule. Science 2008, 321, 259–263. - PubMed
-
- Chhabra S. R.; Harty C.; Hooi D. S. W.; Daykin M.; Williams P.; Pritchard D. I.; Bycroft B. W. Synthetic analogues of bacterial quorum sensing molecules as immune modulators. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 97–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Miscellaneous

