A reliable and cost effective approach for radiographic monitoring in nutritional rickets
- PMID: 24593231
- PMCID: PMC4067015
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20130648
A reliable and cost effective approach for radiographic monitoring in nutritional rickets
Abstract
Objective: Radiological scoring is particularly useful in rickets, where pre-treatment radiographical findings can reflect the disease severity and can be used to monitor the improvement. However, there is only a single radiographic scoring system for rickets developed by Thacher and, to the best of our knowledge, no study has evaluated radiographic changes in rickets based on this scoring system apart from the one done by Thacher himself. The main objective of this study is to compare and analyse the pre-treatment and post-treatment radiographic parameters in nutritional rickets with the help of Thacher's scoring technique.
Methods: 176 patients with nutritional rickets were given a single intramuscular injection of vitamin D (600 000 IU) along with oral calcium (50 mg kg(-1)) and vitamin D (400 IU per day) until radiological resolution and followed for 1 year. Pre- and post-treatment radiological parameters were compared and analysed statistically based on Thacher's scoring system.
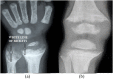
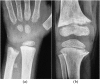
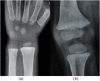
Results: Radiological resolution was complete by 6 months. Time for radiological resolution and initial radiological score were linearly associated on regression analysis. The distal ulna was the last to heal in most cases except when the initial score was 10, when distal femur was the last to heal.
Conclusion: Thacher's scoring system can effectively monitor nutritional rickets. The formula derived through linear regression has prognostic significance.
Advances in knowledge: The distal femur is a better indicator in radiologically severe rickets and when resolution is delayed. Thacher's scoring is very useful for monitoring of rickets. The formula derived through linear regression can predict the expected time for radiological resolution.
Figures


References
-
- Holick MF. Mineral and vitamin D adequacy in infant fed human milk or formula between 6 and 12 months of age. J Pediatr 1994; 117: 134–42. - PubMed
-
- Thacher TD, Fischer PR, Pettifor JM, Lawson JO, Manaster BJ, Reading JC, et al. Radiographic scoring method for the assessment of the severity of nutritional rickets. J Trop Paeditr 2000; 46: 132–9. - PubMed
-
- Pettifor JM. Vitamin D &/or calcium deficiency rickets in infants & children a global perspective. Indian J Med Res 2008; 127: 245–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

