Endoplasmic reticulum protein ERp46 in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 24594673
- PMCID: PMC3940878
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090389
Endoplasmic reticulum protein ERp46 in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
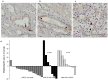
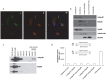
An established inverse clinical correlation between serum adiponectin levels and renal cell carcinoma (RCC) aggressiveness exists. We have recently demonstrated that adiponectin suppresses clear cell RCC (ccRCC) progression through interaction with its receptor, adiponectin receptor 1 (AdipoR1). ERp46 has been shown to inhibit adiponectin signaling via interaction with AdipoR1 in HeLa cells. However, the expression of ERp46 in RCC has not been described thus far. The objectives of this study were to investigate ERp46 in RCC, its expression, its effects on RCC growth in a mouse model and whether it interacts with AdipoR1. We demonstrated a higher ERp46/AdipoR1 expression ratio in metastatic compared to non-metastatic ccRCC, as determined by immunohistochemistry of tissue microarrays and subsequent image analysis. When ERp46 was stably knocked down using shRNA or overexpressed in murine RCC RAG cells, RCC growth after subcutaneous injection in BALB/c nude mice was inhibited and accelerated, respectively. In vitro analysis to determine the molecular interaction between AdipoR1 and ERp46 included co-immunoprecipitation using human ccRCC 786-O cells and a bacterial adenylate cyclase-based two hybrid system and demonstrated no sustained AdipoR1-ERp46 interaction. This is the first report to suggest a role for ERp46 as a potential therapeutic target in RCC given its expression profile in human RCC samples and its effect on in vivo RCC growth. Since a stable interaction with AdipoR1 could not be established, we suggest that the tumorigenic properties of ERp46 in RCC cells are not related to an inhibitory modulation of AdipoR1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Klinghoffer Z, Yang B, Kapoor A, Pinthus JH (2009) Obesity and renal cell carcinoma: epidemiology, underlying mechanisms and management considerations. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 9: 975–987. - PubMed
-
- Diez JJ, Iglesias P (2003) The role of the novel adipocyte-derived hormone adiponectin in human disease. Eur J Endocrinol 148: 293–300. - PubMed
-
- Gavrila A, Chan JL, Yiannakouris N, Kontogianni M, Miller LC, et al. (2003) Serum adiponectin levels are inversely associated with overall and central fat distribution but are not directly regulated by acute fasting or leptin administration in humans: cross-sectional and interventional studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88: 4823–4831. - PubMed
-
- Trujillo ME, Scherer PE (2005) Adiponectin—journey from an adipocyte secretory protein to biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. J Intern Med 257: 167–175. - PubMed
-
- Pinthus JH, Kleinmann N, Tisdale B, Chatterjee S, Lu JP, et al. (2008) Lower plasma adiponectin levels are associated with larger tumor size and metastasis in clear-cell carcinoma of the kidney. Eur Urol 54: 866–873. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

