A five-microRNA panel in plasma was identified as potential biomarker for early detection of gastric cancer
- PMID: 24595006
- PMCID: PMC4007222
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2014.119
A five-microRNA panel in plasma was identified as potential biomarker for early detection of gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) have been implicated as novel biomarkers for gastric cancer (GC) diagnosis. However, the mixture of GC subtypes may have led to the inconsistent circulating miRNA profiles, and the clinical performance of circulating miRNAs has not yet been evaluated independently on early detection of GC.
Methods: A four-phase study was designed with a total of 160 cancer-free controls, 124 patients with gastric non-cardia adenocarcinoma (GNCA) and 36 patients diagnosed gastric cardia adenocarcinoma (GCA). In the discovery phase, we screened the miRNA expression profile in plasma of 40 GNCA patients (stage I) and 40 matched controls by TaqMan low density array (TLDA) chips with pooled samples. Differentially expressed miRNAs were further validated in individual sample using quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR) in the training phase. Subsequently, in an independent validation phase, the identified miRNAs were evaluated in 48 GNCA patients (stage I) and 102 matched controls. Finally, the identified miRNAs were further assessed in an external validation phase including advanced GNCA and GCA patients. Additionally, the expression levels of identified miRNAs were measured in the media of BGC823 and MGC803 cell lines.
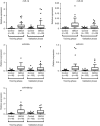
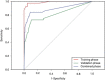
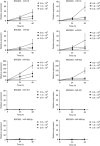
Results: Five miRNAs (miR-16, miR-25, miR-92a, miR-451 and miR-486-5p) showed consistently elevated levels in plasma of the GC patients as compared with controls, and were identified to be potential markers for GNCA with area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (AUCs) ranging from 0.850 to 0.925 and 0.694 to 0.790 in the training and validation phases, respectively. The five-miRNA panel presented a high diagnostic accuracy for the early-stage GNCA (AUCs=0.989 and 0.812 for the training and validation phases, respectively). Three miRNAs (miR-16, miR-25 and miR-92a) were excreted into the culture media of GC cell lines.
Conclusions: The five-miRNA panel in plasma may serve as a potential non-invasive biomarker in detecting the early-stage GC.
Figures
References
-
- Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, Ruf IK, Pritchard CC, Gibson DF, Mitchell PS, Bennett CF, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Stirewalt DL, Tait JF, Tewari M. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108 (12:5003–5008. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bandres E, Bitarte N, Arias F, Agorreta J, Fortes P, Agirre X, Zarate R, Diaz-Gonzalez JA, Ramirez N, Sola JJ, Jimenez P, Rodriguez J, Garcia-Foncillas J. microRNA-451 regulates macrophage migration inhibitory factor production and proliferation of gastrointestinal cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15 (7:2281–2290. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K, Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X, Li Q, Li X, Wang W, Zhang Y, Wang J, Jiang X, Xiang Y, Xu C, Zheng P, Zhang J, Li R, Zhang H, Shang X, Gong T, Ning G, Wang J, Zen K, Zhang J, Zhang CY. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008;18 (10:997–1006. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Hu ZB, Wang WJ, Ba Y, Ma LJ, Zhang CN, Wang C, Ren ZJ, Zhao Y, Wu SJ, Zhuang R, Zhang YX, Hu H, Liu CZ, Xu L, Wang J, Shen HB, Zhang JF, Zen K, Zhang CY. Identification of ten serum microRNAs from a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profile as novel noninvasive biomarkers for nonsmall cell lung cancer diagnosis. Int J Cancer. 2012;130 (7:1620–1628. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127 (12:2893–2917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

