Meta-analysis: the effects of smoking on the disposition of two commonly used antipsychotic agents, olanzapine and clozapine
- PMID: 24595134
- PMCID: PMC3948577
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-004216
Meta-analysis: the effects of smoking on the disposition of two commonly used antipsychotic agents, olanzapine and clozapine
Abstract
Objective: To clarify the effects of smoking on the disposition of two commonly used antipsychotics, olanzapine and clozapine, and to create standards to adjust the doses of these drugs in clinical practice based on the smoking status.
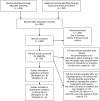
Design: A meta-analysis was conducted by searching MEDLINE, Scopus and the Cochrane Library for relevant prospective and retrospective studies.
Included studies: We included the studies that investigated the effects of smoking on the concentration to dose (C/D) ratio of olanzapine or clozapine.
Primary outcome measure: The weighted mean difference was calculated using a DerSimonian-Laird random effects model, along with 95% CI.
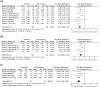
Results: Seven association studies, comprising 1094 patients (652 smokers and 442 non-smokers) with schizophrenia or other psychiatric disorders, were included in the meta-analysis of olanzapine. The C/D ratio was significantly lower in smokers than in non-smokers (p<0.00001), and the mean difference was -0.75 (ng/mL)/(mg/day) (95% CI -0.89 to -0.61). Therefore, it was estimated that if 10 and 20 mg/day of olanzapine would be administered to smokers, about 7 and 14 mg/day, respectively, should be administered to non-smokers in order to obtain the equivalent olanzapine concentration. Four association studies of clozapine were included in the meta-analysis of clozapine, comprising 196 patients (120 smokers and 76 non-smokers) with schizophrenia or other psychiatric disorders. The C/D ratio was significantly lower in smokers than in non-smokers (p<0.00001), and the mean difference was -1.11 (ng/mL)/(mg/day) (95% CI -1.53 to -0.70). Therefore, it was estimated that if 200 and 400 mg/day of clozapine would be administered to smokers, about 100 and 200 mg/day, respectively, should be administered to non-smokers.
Conclusions: We suggest that the doses of olanzapine and clozapine should be reduced by 30% and 50%, respectively, in non-smokers compared with smokers in order to obtain an equivalent olanzapine or clozapine concentration.
Keywords: Mental Health.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of variable cigarette consumption on the interaction with clozapine and olanzapine.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2006 Dec;62(12):1049-53. doi: 10.1007/s00228-006-0209-9. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17089108 Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of tobacco smoking cessation on stable clozapine or olanzapine treatment.Ann Pharmacother. 2010 Apr;44(4):727-32. doi: 10.1345/aph.1M398. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Ann Pharmacother. 2010. PMID: 20233914 Review.
-
Glucose metabolism in patients with schizophrenia treated with atypical antipsychotic agents: a frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test and minimal model analysis.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005 Jan;62(1):19-28. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.1.19. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 15630069
-
Impact of smoking behavior on clozapine blood levels - a systematic review and meta-analysis.Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2020 Dec;142(6):456-466. doi: 10.1111/acps.13228. Epub 2020 Sep 27. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2020. PMID: 32869278
-
Equivalent occupancy of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors with clozapine: differentiation from other atypical antipsychotics.Am J Psychiatry. 2004 Sep;161(9):1620-5. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.161.9.1620. Am J Psychiatry. 2004. PMID: 15337652
Cited by
-
A computer-based quantitative systems pharmacology model of negative symptoms in schizophrenia: exploring glycine modulation of excitation-inhibition balance.Front Pharmacol. 2014 Oct 21;5:229. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00229. eCollection 2014. Front Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25374541 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective Review of Clozapine Use in Children and Adolescents.J Can Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2021 Feb;30(1):36-48. Epub 2021 Feb 1. J Can Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33552171 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiological Determinants of Tobacco Smoking in Schizophrenia.Front Psychiatry. 2018 Dec 6;9:672. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00672. eCollection 2018. Front Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30574101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulated inflammation may predispose patients with serious mental illnesses to severe COVID‑19 (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2021 Aug;24(2):611. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12250. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34184073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unidentified CYP2D6 genotype does not affect pharmacological treatment for patients with first episode psychosis.J Psychopharmacol. 2024 Dec;38(12):1111-1121. doi: 10.1177/02698811241279022. Epub 2024 Sep 29. J Psychopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39344086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mauri MC, Volonteri LS, Colasanti A, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics of atypical antipsychotics: a critical review of the relationship between plasma concentrations and clinical response. Clin Pharmacokinet 2007;46:359–88 - PubMed
-
- Bishara D, Olofinjana O, Sparshatt A, et al. Olanzapine: a systematic review and meta-regression of the relationships between dose, plasma concentration, receptor occupancy, and response. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2013;33:329–35 - PubMed
-
- Bersani FS, Capra E, Minichino A, et al. Factors affecting interindividual differences in clozapine response: a review and case report. Hum Psychopharmacol 2011;26:177–87 - PubMed
-
- Morisano D, Wing VC, Sacco KA, et al. Effects of tobacco smoking on neuropsychological function in schizophrenia in comparison to other psychiatric disorders and non-psychiatric controls. Am J Addict 2013;22:46–53 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical