Natural enemies delay insect resistance to Bt crops
- PMID: 24595158
- PMCID: PMC3940876
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090366
Natural enemies delay insect resistance to Bt crops
Abstract
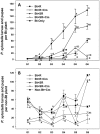
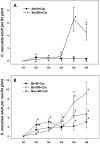
We investigated whether development of resistance to a Bt crop in the presence of a natural enemy would be slower than without the natural enemy and whether biological control, in conjunction with a Bt crop, could effectively suppress the pest population. Additionally, we investigated whether insecticide-sprayed refuges of non-Bt crops would delay or accelerate resistance to the Bt crop. We used a system of Bt broccoli expressing Cry1Ac, a population of the pest Plutella xylostella with a low frequency of individuals resistant to Cry1Ac and the insecticide spinosad, and a natural enemy, Coleomegilla maculata, to conduct experiments over multiple generations. The results demonstrated that after 6 generations P. xylostella populations were very low in the treatment containing C. maculata and unsprayed non-Bt refuge plants. Furthermore, resistance to Bt plants evolved significantly slower in this treatment. In contrast, Bt plants with no refuge were completely defoliated in treatments without C. maculata after 4-5 generations. In the treatment containing sprayed non-Bt refuge plants and C. maculata, the P. xylostella population was low, although the speed of resistance selection to Cry1Ac was significantly increased. These data demonstrate that natural enemies can delay resistance to Bt plants and have significant implications for integrated pest management (IPM) with Bt crops.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pest control and resistance management through release of insects carrying a male-selecting transgene.BMC Biol. 2015 Jul 16;13:49. doi: 10.1186/s12915-015-0161-1. BMC Biol. 2015. PMID: 26179401 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of resistance to transgenic crops: interactions between insect movement and field distribution.J Econ Entomol. 2005 Dec;98(6):1751-62. doi: 10.1093/jee/98.6.1751. J Econ Entomol. 2005. PMID: 16539091
-
Effect of Bt broccoli and resistant genotype of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) on development and host acceptance of the parasitoid Diadegma insulare (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae).Transgenic Res. 2011 Aug;20(4):887-97. doi: 10.1007/s11248-010-9471-9. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Transgenic Res. 2011. PMID: 21181494
-
Management of Insect Pests with Bt Crops in the United States.Annu Rev Entomol. 2023 Jan 23;68:31-49. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-120220-105502. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Annu Rev Entomol. 2023. PMID: 36170641 Review.
-
The progress in insect cross-resistance among Bacillus thuringiensis toxins.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2019 Nov;102(3):e21547. doi: 10.1002/arch.21547. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30864250 Review.
Cited by
-
Translational research in agricultural biology-enhancing crop resistivity against environmental stress alongside nutritional quality.Front Chem. 2014 Jun 5;2:30. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2014.00030. eCollection 2014. Front Chem. 2014. PMID: 24926479 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The presence of Bt-transgenic oilseed rape in wild mustard populations affects plant growth.Transgenic Res. 2015 Dec;24(6):1043-53. doi: 10.1007/s11248-015-9903-7. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Transgenic Res. 2015. PMID: 26338267
-
Life-History Traits of Spodoptera frugiperda Populations Exposed to Low-Dose Bt Maize.PLoS One. 2016 May 31;11(5):e0156608. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156608. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27243977 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout of the HaREase Gene Improves the Stability of dsRNA and Increases the Sensitivity of Helicoverpa armigera to Bacillus thuringiensis Toxin.Front Physiol. 2019 Oct 25;10:1368. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01368. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31708803 Free PMC article.
-
Does prey encounter and nutrient content affect prey selection in wolf spiders inhabiting Bt cotton fields?PLoS One. 2019 Jan 10;14(1):e0210296. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210296. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30629650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shelton AM, Zhao J-Z, Roush RT (2002) Economic, ecological, food safety, and social consequences of the deployment of Bt transgenic Plants. Annu Rev Entomol 47: 845–881. - PubMed
-
- Romeis J, Shelton AM, Kennedy GG (2008) Integration of insect-resistant genetically modified crops within IPM programs. Dordrecht, Springer. 441 pp.
-
- James C (2012) Global status of commercialized transgenic crops: Bt cotton, ISAAA Briefs No. 44. Ithaca, NY: International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications.
-
- Qaim M, Pray CE, Zilberman D (2008) Economic and social considerations in the adoption of Bt crops. In: Romeis J, Shelton AM, Kennedy GG, editors. Integration of insect-resistant genetically modified crops within IPM programs. Dordrecht: Springer. pp 329–356.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

