The microRNA miR-34a inhibits non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) growth and the CD44hi stem-like NSCLC cells
- PMID: 24595209
- PMCID: PMC3942411
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090022
The microRNA miR-34a inhibits non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) growth and the CD44hi stem-like NSCLC cells
Abstract
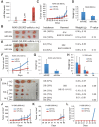
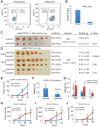
Lung cancer is among the most lethal malignancies with a high metastasis and recurrence rate, which is probably due to the existence of lung cancer stem cells (CSCs). CSCs in many tumors including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have been identified using adhesion molecular CD44, either individually or in combination with other marker(s). MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate both normal stem cells and CSCs and dysregulation of miRNAs has been implicated in tumorigenesis. Recently, miR-34a was found to be downregulated in NSCLC cells but the biological functions of miR-34a in regulating NSCLC cell behavior have not been extensively studied. Here we show that transfection of synthetic miR-34a, but not the negative control (NC) miRNA oligonucleotides (oligos) in three NSCLC cell lines, i.e., A549, H460, and H1299, inhibited their holoclone formation, clonogenic expansion, and tumor regeneration in vivo. Furthermore, the lentiviral vector-mediated overexpression of miR-34a in purified CD44hi H460 cells also inhibited tumor outgrowth. In contrast, expression of miR-34a antagomirs (i.e., antisense oligos) in the CD44lo H460 cells promoted tumor development. Our study shows that miR-34a is a negative regulator of the tumorigenic properties of NSCLC cells and CD44hi lung CSCs, and establishes a strong rationale for developing miR-34a as a novel therapeutic agent against NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by directly repressing CD44.Nat Med. 2011 Feb;17(2):211-5. doi: 10.1038/nm.2284. Epub 2011 Jan 16. Nat Med. 2011. PMID: 21240262 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA DGCR5 contributes to CSC-like properties via modulating miR-330-5p/CD44 in NSCLC.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Sep;233(9):7447-7456. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26590. Epub 2018 Apr 16. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29663359
-
Acacetin inhibited non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell growth via upregulating miR-34a in vitro and in vivo.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 29;14(1):2348. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52896-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38287075 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of tumor suppressing microRNAs as therapeutics in managing non-small cell lung cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Apr;256:155222. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155222. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38452582 Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in non-small cell lung cancer stemness and clinical applications.Front Immunol. 2024 May 3;15:1369356. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1369356. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38765006 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreatic cancer stem cells.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Feb 15;5(3):894-906. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26045976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiproliferative effect of upregulation of hsa-let-7c-5p in human acute erythroleukemia cells.Cytotechnology. 2018 Dec;70(6):1509-1518. doi: 10.1007/s10616-018-0241-5. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Cytotechnology. 2018. PMID: 30073438 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of cell cycle genes in cancer: unmasking the role of cancer stem cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Apr;47(4):3065-3076. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05341-6. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32112300 Review.
-
Therapeutic use of microRNAs in lung cancer.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:756975. doi: 10.1155/2014/756975. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25309923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) enhances tumor growth and cancer stemness of HPV-negative oral/oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells via miR-181 regulation.Papillomavirus Res. 2015 Dec 1;1:116-125. doi: 10.1016/j.pvr.2015.08.001. Papillomavirus Res. 2015. PMID: 26693182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144: 646–674. - PubMed
-
- Garofalo M, Croce CM (2011) MicroRNAs: Master regulators as potential therapeutics in cancer. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 51: 25–43. - PubMed
-
- Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ, Parker R (2006) Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev 20: 515–524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

