Shared signaling systems in myeloid cell-mediated muscle regeneration
- PMID: 24595286
- PMCID: PMC3943178
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.098285
Shared signaling systems in myeloid cell-mediated muscle regeneration
Abstract
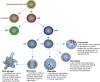
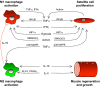
Much of the focus in muscle regeneration has been placed on the identification and delivery of stem cells to promote regenerative capacity. As those efforts have advanced, we have learned that complex features of the microenvironment in which regeneration occurs can determine success or failure. The immune system is an important contributor to that complexity and can determine the extent to which muscle regeneration succeeds. Immune cells of the myeloid lineage play major regulatory roles in tissue regeneration through two general, inductive mechanisms: instructive mechanisms that act directly on muscle cells; and permissive mechanisms that act indirectly to influence regeneration by modulating angiogenesis and fibrosis. In this article, recent discoveries that identify inductive actions of specific populations of myeloid cells on muscle regeneration are presented, with an emphasis on how processes in muscle and myeloid cells are co-regulated.
Keywords: Macrophage phenotype; Muscle regeneration; Signaling systems.
Figures

References
-
- Allen R. E., Boxhorn L. K. (1989). Regulation of skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by transforming growth factor-beta, insulin-like growth factor I, and fibroblast growth factor. J. Cell. Physiol. 138, 311–315 - PubMed
-
- Alter J., Rozentzweig D., Bengal E. (2008). Inhibition of myoblast differentiation by tumor necrosis factor alpha is mediated by c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 and leukemia inhibitory factor. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 23224–23234 - PubMed
-
- Badylak S. F., Valentin J. E., Ravindra A. K., McCabe G. P., Stewart-Akers A. M. (2008). Macrophage phenotype as a determinant of biologic scaffold remodeling. Tissue Eng. Part A 14, 1835–1842 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

