Mineralocorticoid receptor signaling reduces numbers of circulating human naïve T cells and increases their CD62L, CCR7, and CXCR4 expression
- PMID: 24595810
- PMCID: PMC4298762
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201344265
Mineralocorticoid receptor signaling reduces numbers of circulating human naïve T cells and increases their CD62L, CCR7, and CXCR4 expression
Abstract
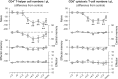
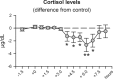
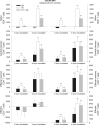
The role of mineralocorticoid receptors (MRs) in human T-cell migration is not yet understood. We have recently shown that the MR antagonist spironolactone selectively increases the numbers of circulating naïve and central memory T cells during early sleep, which is the time period in the 24 h cycle hallmarked by predominant MR activation. To investigate whether this effect is specific to spironolactone's blockade of MRs and to study the underlying molecular mechanisms, healthy humans were given the selective MR-agonist fludrocortisone or placebo and numbers of eight T-cell subsets and their CD62L and CXCR4 expression were analyzed. Fludrocortisone selectively reduced counts of naïve CD4(+) , central memory CD4(+), and naïve CD8(+) T cells and increased CXCR4 expression on the naïve subsets. In complementing in vitro studies, fludrocortisone enhanced CXCR4 and CD62L expression, which was counteracted by spironolactone. Incubation of naïve T cells with spironolactone alone reduced CD62L and CCR7 expression. Our results indicate a regulatory influence of MR signaling on human T-cell migration and suggest a role for endogenous aldosterone in the redistribution of T-cell subsets to lymph nodes, involving CD62L, CCR7, and CXCR4. Facilitation of T-cell homing following sleep-dependent aldosterone release might thus essentially contribute to sleep's well-known role in supporting adaptive immunity.
Keywords: CD62L; CXCR4; Mineralocorticoid receptor; Naïve T cells; Sleep.
© 2014 The Authors. European Journal of Immunology published by WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Blockade of mineralocorticoid receptors enhances naïve T-helper cell counts during early sleep in humans.Brain Behav Immun. 2012 Oct;26(7):1116-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.07.016. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Brain Behav Immun. 2012. PMID: 22884414 Clinical Trial.
-
Cortisol increases CXCR4 expression but does not affect CD62L and CCR7 levels on specific T cell subsets in humans.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Jun 1;306(11):E1322-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00678.2013. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24760986 Clinical Trial.
-
Analysis of naïve lung CD4 T cells provides evidence of functional lung to lymph node migration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 29;110(5):1821-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1221306110. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23319636 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of CC-chemokine receptor 7 expression on murine T cells in lymphoid tissues.Immunology. 2003 Oct;110(2):170-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01727.x. Immunology. 2003. PMID: 14511230 Free PMC article.
-
[Subpopulations and cytokine expression of naïve and memory T cells in normal human PBMCs].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007 Jan;23(1):2-5. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 17210094 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Regulation of the germinal center response by nuclear receptors and implications for autoimmune diseases.FEBS J. 2020 Jul;287(14):2866-2890. doi: 10.1111/febs.15312. Epub 2020 Apr 19. FEBS J. 2020. PMID: 32246891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased Rates of Septic Shock, Cardiac Arrest, and Mortality Associated With Chronic Steroid Use Following Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion for Cervical Stenosis.Int J Spine Surg. 2020 Oct;14(5):649-656. doi: 10.14444/7095. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Int J Spine Surg. 2020. PMID: 33046542 Free PMC article.
-
Mineralocorticoid Receptor and Aldosterone-Related Biomarkers of End-Organ Damage in Cardiometabolic Disease.Biomolecules. 2018 Sep 18;8(3):96. doi: 10.3390/biom8030096. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 30231508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulation and immunopharmacology in heart failure.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024 Feb;21(2):119-149. doi: 10.1038/s41569-023-00919-6. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 37709934 Review.
-
Distribution and Abundance of Glucocorticoid and Mineralocorticoid Receptors throughout the Brain of the Great Tit (Parus major).PLoS One. 2016 Feb 11;11(2):e0148516. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148516. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26867218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ottaway CA, Husband AJ. Central nervous system influences on lymphocyte migration. Brain Behav. Immun. 1992;6:97–116. - PubMed
-
- Dhabhar FS, Miller AH, Stein M, McEwen BS, Spencer RL. Diurnal and acute stress-induced changes in distribution of peripheral blood leukocyte subpopulations. Brain Behav. Immun. 1994;8:66–79. - PubMed
-
- Dhabhar FS, Miller AH, McEwen BS, Spencer RL. Stress-induced changes in blood leukocyte distribution. Role of adrenal steroid hormones. J. Immunol. 1996;157:1638–1644. - PubMed
-
- Trifonova ST, Zimmer J, Turner JD, Muller CP. Diurnal redistribution of human lymphocytes and their temporal associations with salivary cortisol. Chronobiol. Int. 2013;30:669–681. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

