TTC26/DYF13 is an intraflagellar transport protein required for transport of motility-related proteins into flagella
- PMID: 24596149
- PMCID: PMC3936282
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.01566
TTC26/DYF13 is an intraflagellar transport protein required for transport of motility-related proteins into flagella
Erratum in
-
Correction: TTC26/DYF13 is an intraflagellar transport protein required for transport of motility-related proteins into flagella.Elife. 2014 Apr 1;3:e02897. doi: 10.7554/eLife.02897. Elife. 2014. PMID: 24692455 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
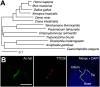
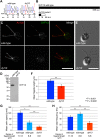
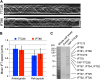
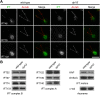
Cilia/flagella are assembled and maintained by the process of intraflagellar transport (IFT), a highly conserved mechanism involving more than 20 IFT proteins. However, the functions of individual IFT proteins are mostly unclear. To help address this issue, we focused on a putative IFT protein TTC26/DYF13. Using live imaging and biochemical approaches we show that TTC26/DYF13 is an IFT complex B protein in mammalian cells and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Knockdown of TTC26/DYF13 in zebrafish embryos or mutation of TTC26/DYF13 in C. reinhardtii, produced short cilia with abnormal motility. Surprisingly, IFT particle assembly and speed were normal in dyf13 mutant flagella, unlike in other IFT complex B mutants. Proteomic and biochemical analyses indicated a particular set of proteins involved in motility was specifically depleted in the dyf13 mutant. These results support the concept that different IFT proteins are responsible for different cargo subsets, providing a possible explanation for the complexity of the IFT machinery. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.01566.001.
Keywords: Chlamydomonas; axoneme; dynein; flagella.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Comment in
-
Boarder control on the IFT train.Elife. 2014 Mar 18;3:e02531. doi: 10.7554/eLife.02531. Elife. 2014. PMID: 24642415 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

