Does the cis/trans configuration of peptide bonds in bioactive tripeptides play a role in ACE-1 enzyme inhibition?
- PMID: 24596454
- PMCID: PMC3930482
- DOI: 10.2147/BTT.S54056
Does the cis/trans configuration of peptide bonds in bioactive tripeptides play a role in ACE-1 enzyme inhibition?
Abstract
Background: The milk casein-derived bioactive tripeptides isoleucine-proline-proline (IPP) and valine-proline-proline (VPP) have been shown to prevent development of hypertension in animal models and to lower blood pressure in moderately hypertensive subjects in most but not all clinical trials. Inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme 1 (ACE-1) has been suggested as the explanation for these antihypertensive and beneficial vascular effects. Previously, human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) have not been used to test ACE-1 inhibiting properties of casein derived tripeptides in vasculature.
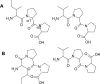
Purpose: We focused on the cis/trans configurations of the peptide bonds in proline-containing tripeptides in order to discover whether the different structural properties of these peptides influence their activity in ACE-1 inhibition. We hypothesized that the configuration of proline-containing peptides plays a significant role in enzyme inhibition.
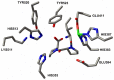
Methods: AutoDock 4.2 docking software was used to predict suitable peptide bond configurations of the tripeptides. Besides modeling studies, we completed ACE-1 activity measurements in vitro using HUVEC cultures.
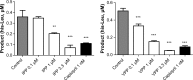
Results: In HUVEC cells, both IPP and VPP inhibited ACE-1. Based on molecular docking studies, we propose that in ACE-1 inhibition IPP and VPP share a similar cis configuration between the first aliphatic (isoleucine or valine) and the second (proline) amino acid residues and more different configurations between two proline residues. In vivo experiments are needed to validate the significance of the present findings.
Keywords: ACE inhibition; Autodock modeling; Ile-Pro-Pro; Val-Pro-Pro; vascular function.
Figures


References
-
- Turpeinen AM, Järvenpää S, Kautiainen H, Korpela R, Vapaatalo H. Antihypertensive effects of bioactive tripeptides – a random effects meta-analysis. Ann Med. 2013;45(1):51–56. - PubMed
-
- Luhtala S, Vaajanen A, Oksala O, Valjakka J, Vapaatalo H. Activities of angiotensin-converting enzymes 1 (ACE1) and 2 (ACE2) and inhibition by bioactive peptides in porcine ocular tissues. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009;25(1):23–28. - PubMed
-
- Sipola M, Finckenberg P, Santisteban J, Korpela R, Vapaatalo H, Nurminen ML. Long-term intake of milk peptide attenuates development of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2001;52(4 Pt2):745–754. - PubMed
-
- Jäkälä P, Hakala A, Turpeinen AM, Korpela R, Vapaatalo H. Casein-derived bioactive tripeptides Ile-Pro-Pro and Val-Pro-Pro attenuate the development of hypertension and improve endothelial function in salt-loaded Goto-Kakizaki rats. J Funct Foods. 2009;1(4):366–374.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

