Efficacy and safety of coadministration of once-daily indacaterol and glycopyrronium versus indacaterol alone in COPD patients: the GLOW6 study
- PMID: 24596459
- PMCID: PMC3940646
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S51592
Efficacy and safety of coadministration of once-daily indacaterol and glycopyrronium versus indacaterol alone in COPD patients: the GLOW6 study
Abstract
Background: Addition of a second bronchodilator from a different pharmacological class may benefit patients with moderate-to-severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) whose symptoms are insufficiently controlled by bronchodilator monotherapy. GLOW6 evaluated the efficacy and safety of once-daily coadministration of the long-acting β2-agonist indacaterol (IND) and the long-acting muscarinic antagonist glycopyrronium (GLY) versus IND alone in patients with moderate-to-severe COPD.
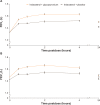
Materials and methods: In this randomized, double-blind, parallel group, placebo-controlled, 12-week study, patients were randomized 1:1 to IND 150 μg and GLY 50 μg daily (IND + GLY) or IND 150 μg daily and placebo (IND + PBO) (all delivered via separate Breezhaler® devices). The primary objective was to demonstrate the superiority of IND + GLY versus IND + PBO for trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) at week 12. Other end points included trough FEV1 at day 1, FEV1 area under the curve from 30 minutes to 4 hours (AUC30min-4h), peak FEV1, inspiratory capacity and trough forced vital capacity (FVC) at day 1 and week 12, and transition dyspnea index (TDI) focal score, COPD symptoms, and rescue medication use over 12 weeks.
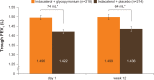
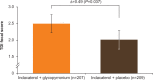
Results: A total of 449 patients were randomized (IND + GLY, 226; IND + PBO, 223); 94% completed the study. On day 1 and at week 12, IND + GLY significantly improved trough FEV1 versus IND + PBO, with treatment differences of 74 mL (95% CI 46-101 mL) and 64 mL (95% CI 28-99 mL), respectively (both P<0.001). IND + GLY significantly improved postdose peak FEV1, FEV1 AUC30min-4h, and trough FVC at day 1 and week 12 versus IND + PBO (all P<0.01). TDI focal score and COPD symptoms (percentage of days able to perform usual daily activities and change from baseline in mean daytime respiratory score) were significantly improved with IND + GLY versus IND + PBO (P<0.05). The incidence of adverse events was similar for the two treatment groups.
Conclusion: In patients with moderate-to-severe COPD, once-daily coadministration of IND and GLY provides significant and sustained improvement in bronchodilation versus IND alone from day 1, with significant improvements in patient-centered outcomes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01604278.
Keywords: Breezhaler®; COPD; bronchodilation; glycopyrronium; indacaterol; inhalation therapy.
Figures


References
-
- Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD, Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) 2013. [Accessed on January 8, 2014]. Available from: http://www.goldcopd.org/
-
- Cazzola M, Matera MG. Long-acting bronchodilators are the first-choice option for the treatment of stable COPD. Chest. 2004;125(1):9–11. - PubMed
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA) Seebri Breezhaler (glycopyrronium bromide: summary of product characteristics. [Accessed June 25, 2013]. Available from: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Info....
-
- Novartis Global . Novartis receives European Commission approval for once-daily Seebri® Breezhaler® as maintenance COPD treatment in the EU [press release] Basel, Switzerland: Novartis; 2012. [Accessed 22 November, 2012]. [October 1]. Available from: http://www.novartis.com/newsroom/media-releases/en/2012/1645116.shtml.
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA) Bretaris Genuair (aclidinium bromide): summary of product characteristics. [Accessed June 25, 2013]. Available from: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Info....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

