Recombinant expression and purification of human placental growth factor 1 and specific camel heavy chain polyclonal antibody preparation
- PMID: 24596498
- PMCID: PMC3937466
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2013.04.008
Recombinant expression and purification of human placental growth factor 1 and specific camel heavy chain polyclonal antibody preparation
Abstract
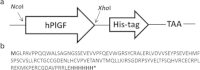
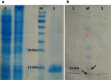
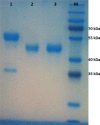
Placental growth factor (PlGF) is a member of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family. Unlike VEGF, PlGF is dispensable for normal cell development as well as playing various roles in pathological angiogenesis which occurs in tissue ischemia, inflammation, and malignancy. The PlGF-1 has been considered as a potential candidate for the diagnosis and targeting of pathological angiogenesis. Camelidae serum contains an important fraction of functional antibodies, called heavy-chain antibodies (HcAbs) that are naturally devoid of light chains. Camelid HcAbs recognize their cognate antigens by a single variable-domain, referred to as VHH or Nanobody. Here, we describe the expression and purification of recombinant human PlGF-1 (rhPlGF-1). This protein was subsequently used for the preparation of camel heavy chain polyclonal antibody against rhPlGF-1. The recombinant expression plasmid pET-26b-hPlGF-1 was introduced into Escherichia coli BL21 cells to express the rhPlGF-1 protein. Purified rhPlGF-1 was used to immunize camel, the specific reactivity of HcAb was determined with ELISA and western blot. Western blot analysis indicated that the antiserum specifically reacted to the recombinant protein. The rhPlGF-1 protein and its antibody may be used for the development of detection assays needed for clinical research.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Heavy chain antibody; PlGF; Polyclonal antibody; VHH.
Figures
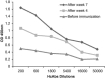
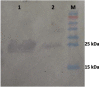

References
-
- Behdani M., Zeinali S., Khanahmad H., Karimipour M., Asadzadeh N., Azadmanesh K., Khabiri A., Schoonooghe S., Habibi Anbouhi M., Hassanzadeh-Ghassabeh G., Muyldermans S. Generation and characterization of a functional Nanobody against the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2; angiogenesis cell receptor. Mol. Immunol. 2012;50:35–41. - PubMed
-
- Bikfalvi A. Angiogenesis and invasion in cancer. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2012;104:35–43. - PubMed
-
- Cortez-Retamozo V., Lauwereys M., Hassanzadeh Gh., Gobert G., Conrath K., Muyldermans S., De Baetselier P., Revets H. Efficient tumor targeting by single-domain antibody fragments of camels. Int. J. Cancer. 2002;98:456–462. - PubMed
-
- Fischer C., Mazzone M., Jonckx B., Carmeliet P. FLT1 and its ligands VEGFB and PlGF: drug targets for anti-angiogenic therapy? Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2008;8:942–956. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis: an organizing principle for drug discovery? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007;6:273–286. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

