Increased drug resistance is associated with reduced glucose levels and an enhanced glycolysis phenotype
- PMID: 24597478
- PMCID: PMC4080979
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12668
Increased drug resistance is associated with reduced glucose levels and an enhanced glycolysis phenotype
Abstract
Background and purpose: The testing of anticancer compounds in vitro is usually performed in hyperglycaemic cell cultures, although many tumours and their in vivo microenvironments are hypoglycaemic. Here, we have assessed, in cultures of tumour cells, the effects of reduced glucose levels on resistance to anticancer drugs and investigated the underlying cellular mechanisms.
Experimental approach: PIK3CA mutant (AGS, HGC27), and wild-type (MKN45, NUGC4) gastric cancer cells were cultured in high-glucose (HG, 25 mM) or low-glucose (LG, 5 mM) media and tested for sensitivity to two cytotoxic compounds, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and carboplatin, the PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, PI103 and the mTOR inhibitor, Ku-0063794.
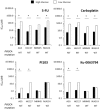
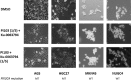
Key results: All cells had increased resistance to 5-FU and carboplatin when cultured in LG compared with HG conditions despite having similar growth and cell cycle characteristics. On treatment with PI103 or Ku-0063794, only the PIK3CA mutant cells displayed increased resistance in LG conditions. The PIK3CA mutant LG cells had selectively increased p-mTOR, p-S6, p-4EBP1, GLUT1 and lactate production, and reduced reactive oxygen species, consistent with increased glycolysis. Combination analysis indicated PI103 and Ku-0063794 were synergistic in PIK3CA mutant LG cells only. Synergism was accompanied by reduced mTOR signalling and increased autophagy.
Conclusions and implications: Hypoglycaemia increased resistance to cytotoxic agents, especially in tumour cells with a high dependence on glycolysis. Dual inhibition of the PI3K/mTOR pathway may be able to attenuate such hypoglycaemia-associated resistance.
Keywords: PI3K; chemoresistance; glycolysis; hypoglycaemia; metabolism.
© 2014 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures




References
-
- Airley RE, Mobasheri A. Hypoxic regulation of glucose transport, anaerobic metabolism and angiogenesis in cancer: novel pathways and targets for anticancer therapeutics. Chemotherapy. 2007;53:233–256. - PubMed
-
- Alexander A, Walker CL. The role of LKB1 and AMPK in cellular responses to stress and damage. FEBS Lett. 2011;585:952–957. - PubMed
-
- Berardi R, Scartozzi M, Romagnoli E, Antognoli S, Cascinu S. Gastric cancer treatment: a systematic review. Oncol Rep. 2004;11:911–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

