5-HT neurons of the area postrema become c-Fos-activated after increases in plasma sodium levels and transmit interoceptive information to the nucleus accumbens
- PMID: 24598462
- PMCID: PMC4010663
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00563.2013
5-HT neurons of the area postrema become c-Fos-activated after increases in plasma sodium levels and transmit interoceptive information to the nucleus accumbens
Abstract
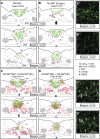
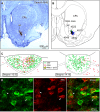
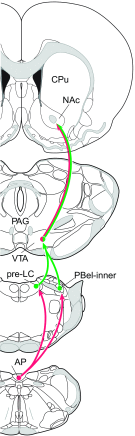
Serotonergic (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) neurons of the area postrema (AP) represent one neuronal phenotype implicated in the regulation of salt appetite. Tryptophan hydroxylase (Tryp-OH, synthetic enzyme-producing 5-HT) immunoreactive neurons in the AP of rats become c-Fos-activated following conditions in which plasma sodium levels are elevated; these include intraperitoneal injections of hypertonic saline and sodium repletion. Non-Tryp-OH neurons also became c-Fos-activated. Sodium depletion, which induced an increase in plasma osmolality but caused no significant change in the plasma sodium concentration, had no effect on the c-Fos activity in the AP. Epithelial sodium channels are expressed in the Tryp-OH-immunoreactive AP neurons, possibly functioning in the detection of changes in plasma sodium levels. Since little is known about the neural circuitry of these neurons, we tested whether the AP contributes to a central pathway that innervates the reward center of the brain. Stereotaxic injections of pseudorabies virus were made in the nucleus accumbens (NAc), and after 4 days, this viral tracer produced retrograde transneuronal labeling in the Tryp-OH and non-Tryp-OH AP neurons. Both sets of neurons innervate the NAc via a multisynaptic pathway. Besides sensory information regarding plasma sodium levels, the AP→NAc pathway may also transmit other types of chemosensory information, such as those related to metabolic functions, food intake, and immune system to the subcortical structures of the reward system. Because these subcortical regions ultimately project to the medial prefrontal cortex, different types of chemical signals from visceral systems may influence affective functions.
Keywords: area postrema; circumventricular organs; epithelial sodium channels; nucleus accumbens; ventral tegmental area.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Blockade of ENaCs by amiloride induces c-Fos activation of the area postrema.Brain Res. 2015 Mar 19;1601:40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.12.048. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25557402 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonergic inputs to FoxP2 neurons of the pre-locus coeruleus and parabrachial nuclei that project to the ventral tegmental area.Neuroscience. 2011 Oct 13;193:229-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.008. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21784133 Free PMC article.
-
Area postrema projects to FoxP2 neurons of the pre-locus coeruleus and parabrachial nuclei: brainstem sites implicated in sodium appetite regulation.Brain Res. 2010 Nov 4;1359:116-27. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.08.085. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20816675 Free PMC article.
-
Using c-fos to study neuronal ensembles in corticostriatal circuitry of addiction.Brain Res. 2015 Dec 2;1628(Pt A):157-73. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.11.005. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25446457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reward Circuitry Plasticity in Pain Perception and Modulation.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Nov 21;8:790. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00790. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29209204 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential effects of mineralocorticoid and angiotensin II on incentive and mesolimbic activity.Horm Behav. 2016 Mar;79:28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.12.002. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Horm Behav. 2016. PMID: 26730722 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of ENaCs by amiloride induces c-Fos activation of the area postrema.Brain Res. 2015 Mar 19;1601:40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.12.048. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25557402 Free PMC article.
-
Embracing diversity in the 5-HT neuronal system.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019 Jul;20(7):397-424. doi: 10.1038/s41583-019-0151-3. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30948838 Review.
-
Optogenetic activation of 5-HT neurons in the dorsal raphe suppresses seizure-induced respiratory arrest and produces anticonvulsant effect in the DBA/1 mouse SUDEP model.Neurobiol Dis. 2018 Feb;110:47-58. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Neurobiol Dis. 2018. PMID: 29141182 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium Homeostasis, a Balance Necessary for Life.Nutrients. 2023 Jan 12;15(2):395. doi: 10.3390/nu15020395. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36678265 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Borison HL, Brizzee KR. Morphology of emetic chemoreceptor trigger zone in cat medulla oblongata. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 77: 38–42, 1951 - PubMed
-
- Cunningham ET, Jr, Miselis RR, Sawchenko PE. The relationship of efferent projections from the area postrema to vagal motor and brain stem catecholamine-containing cell groups: an axonal transport and immunohistochemical study in the rat. Neuroscience 58: 635–648, 1994 - PubMed
-
- De Gobbi JI, Barbosa SP, De Luca LA, Jr, Thunhorst RL, Johnson AK, Menani JV. Activation of serotonergic 5-HT1A receptors in the lateral parabrachial nucleus increases NaCl intake. Brain Res 1066: 1–9, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

