The SAMPL4 host-guest blind prediction challenge: an overview
- PMID: 24599514
- PMCID: PMC4053502
- DOI: 10.1007/s10822-014-9735-1
The SAMPL4 host-guest blind prediction challenge: an overview
Abstract
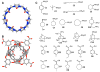
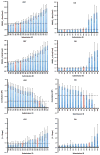
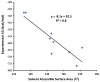
Prospective validation of methods for computing binding affinities can help assess their predictive power and thus set reasonable expectations for their performance in drug design applications. Supramolecular host-guest systems are excellent model systems for testing such affinity prediction methods, because their small size and limited conformational flexibility, relative to proteins, allows higher throughput and better numerical convergence. The SAMPL4 prediction challenge therefore included a series of host-guest systems, based on two hosts, cucurbit[7]uril and octa-acid. Binding affinities in aqueous solution were measured experimentally for a total of 23 guest molecules. Participants submitted 35 sets of computational predictions for these host-guest systems, based on methods ranging from simple docking, to extensive free energy simulations, to quantum mechanical calculations. Over half of the predictions provided better correlations with experiment than two simple null models, but most methods underperformed the null models in terms of root mean squared error and linear regression slope. Interestingly, the overall performance across all SAMPL4 submissions was similar to that for the prior SAMPL3 host-guest challenge, although the experimentalists took steps to simplify the current challenge. While some methods performed fairly consistently across both hosts, no single approach emerged as consistent top performer, and the nonsystematic nature of the various submissions made it impossible to draw definitive conclusions regarding the best choices of energy models or sampling algorithms. Salt effects emerged as an issue in the calculation of absolute binding affinities of cucurbit[7]uril-guest systems, but were not expected to affect the relative affinities significantly. Useful directions for future rounds of the challenge might involve encouraging participants to carry out some calculations that replicate each others' studies, and to systematically explore parameter options.
Figures
References
-
- Kitchen DB, Decornez H, Furr JR, Bajorath J. Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: methods and applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3(11):935–949. - PubMed
-
- Warren GL, Andrews CW, Capelli A-M, Clarke B, LaLonde J, Lambert MH, Lindvall M, Nevins N, Semus SF, Senger S. A critical assessment of docking programs and scoring functions. J Med Chem. 2006;49(20):5912–5931. - PubMed
-
- Gilson MK, Zhou H-X. Calculation of protein-ligand binding affinities. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2007;36:21–42. - PubMed
-
- Guthrie JP. A blind challenge for computational solvation free energies: introduction and overview. J Phys Chem B. 2009;113(14):4501–4507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

