Nasopharyngeal microbiota in healthy children and pneumonia patients
- PMID: 24599973
- PMCID: PMC3993659
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.03280-13
Nasopharyngeal microbiota in healthy children and pneumonia patients
Erratum in
-
Correction for Sakwinska et al., "Nasopharyngeal Microbiota in Healthy Children and Pneumonia Patients".J Clin Microbiol. 2019 May 24;57(6):e00417-19. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00417-19. Print 2019 Jun. J Clin Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31127009 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
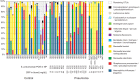
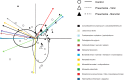
Our study is the first to compare the nasopharyngeal microbiota of pediatric pneumonia patients and control children by 454 pyrosequencing. A distinct microbiota was associated with different pneumonia etiologies. Viral pneumonia was associated with a high abundance of the operational taxonomic unit (OTU) corresponding to Moraxella lacunata. Patients with nonviral pneumonia showed high abundances of OTUs of three typical bacterial pathogens, Streptococcus pneumoniae complex, Haemophilus influenzae complex, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Patients classified as having no definitive etiology harbored microbiota particularly enriched in the H. influenzae complex. We did not observe a commensal taxon specifically associated with health. The microbiota of the healthy nasopharynx was more diverse and contained a wider range of less abundant taxa.
Figures

References
-
- Feigin R, Cherry J, Demmler-Harrison GJ, Kaplan SL. 2009. Feigin and Cherry's textbook of pediatric infectious diseases. Saunders, Philidelphia, PA
-
- Levine OS, O'Brien KL, Deloria-Knoll M, Murdoch DR, Feikin DR, Deluca AN, Driscoll AJ, Baggett HC, Brooks WA, Howie SRC, Kotloff KL, Madhi SA, Maloney SA, Sow S, Thea DM, Scott JA. 2012. The Pneumonia Etiology Research for Child Health Project: a 21st century childhood pneumonia etiology study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 54(Suppl 2):S93–S101. 10.1093/cid/cir1052 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cevey-Macherel M, Galetto-Lacour A, Gervaix A, Siegrist CA, Bille J, Bescher-Ninet B, Kaiser L, Krahenbuhl JD, Gehri M. 2009. Etiology of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children based on WHO clinical guidelines. Eur. J. Pediatr. 168:1429–1436. 10.1007/s00431-009-0943-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

