Cutaneous hypoesthesia following plate fixation in clavicle fractures
- PMID: 24600056
- PMCID: PMC3931138
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5413.125478
Cutaneous hypoesthesia following plate fixation in clavicle fractures
Abstract
Background: We report the functional impact and natural history of cutaneous hypoesthesia after plate internal fixation for mid shaft clavicle fractures with a horizontal skin incision from year 2009 to 2011.
Materials and methods: 38 patients had complete followup data with an average followup period of 23.2 months (range 8-43 months). The impact of supraclavicular nerve injury was studied by assessment of the incidence, functional impact and natural history of numbness with detailed review of the case records and phone questionnaires.
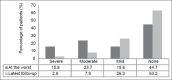
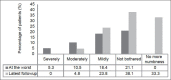
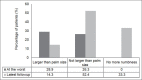
Results: The incidence of postoperative numbness was 55.3% (n = 21). Most patients reported the numbness to be at its worst within the first operative month. At the time of worst numbness, 28.6% (n = 6/21) of patients reported the numbness to be severe while 42.9% (n = 9/21) reported moderate numbness and 28.6% (n = 6/21) reported mild numbness. Fifteen of these patients described increased awareness of numbness during contact with straps or clothes. Two patients were significantly bothered by this numbness; 4 patients stated that it was a moderate bother while 7 patients considered it a mild bother. A total of 8 patients reported that they were not bothered at all by the numbness. An overwhelming majority of affected patients (90.5%, n = 19/21) reported an improvement in the severity of numbness felt over time. At the last followup, the incidence of numbness declined from 55.3% to 36.8% with 7 patients reporting complete resolution of numbness. The numbness however was found to persist in 66.7% of patients. Only 1 patient reported continued severe numbness. The awareness of numbness with straps and clothing was severe in 5 patients. None of the patients were significantly bothered by this numbness.
Conclusions: Cutaneous sensory loss is a common occurrence following plate fixation of the clavicle and might have been under reported in the literature. The numbness improves in the vast majority, but commonly persists to some degree for up to 2 years and maybe permanent. However, only a small minority eventually considered the numbness a significant "bother" and to affect them while wearing clothing or when in contact with shoulder straps.
Keywords: Clavicle fracture; cutaneous hypoesthesia; numbness; supraclavicular nerve; surgical fixation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Shen WJ, Liu TJ, Shen YS. Plate fixation of fresh displaced midshaft clavicle fractures. Injury. 1999;30:497–500. - PubMed
-
- Borley NR, Edwards D, Villar RN. Lateral skin flap numbness after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1995;10:13–4. - PubMed
-
- Hopton BP, Tommichan MC, Howell FR. Reducing lateral skin flap numbness after total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2004;11:289–91. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
