p104 binds to Rac1 and reduces its activity during myotube differentiation of C2C12 cell
- PMID: 24600331
- PMCID: PMC3926281
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/592450
p104 binds to Rac1 and reduces its activity during myotube differentiation of C2C12 cell
Abstract
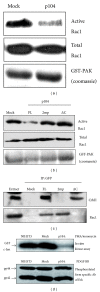
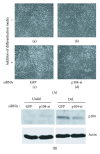
The p104 protein inhibits cellular proliferation when overexpressed in NIH3T3 cells and has been shown to associate with p85α, Grb2, and PLCγ1. In order to isolate other proteins that interact with p104, yeast two-hybrid screening was performed. Rac1 was identified as a binding partner of p104 and the interaction between p104 and Rac1 was confirmed by immunoprecipitation. Using a glutathione S-transferase (GST) pull-down assay with various p104 fragments, the 814-848 amino acid residue at the carboxyl-terminal region of p104 was identified as the key component to interact with Rac1. The CrkII which is involved in the Rac1-mediated cellular response was also found to interact with p104 protein. NIH3T3 cells which overexpressed p104 showed a decrease of Rac1 activity. However, neither the proline-rich domain mutant, which is unable to interact with CrkII, nor the carboxy-terminal deletion mutant could attenuate Rac1 activity. During the differentiation of myoblasts, the amount of p104 protein as well as transcript level was increased. The overexpression of p104 enhanced myotube differentiation, whereas siRNA of p104 reversed this process. In this process, more Rac1 and CrkII were bound to increased p104. Based on these results, we conclude that p104 is involved in muscle cell differentiation by modulating the Rac1 activity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Novel p104 protein regulates cell proliferation through PI3K inhibition and p27(Kip1) expression.BMB Rep. 2010 Mar;43(3):199-204. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2010.43.3.199. BMB Rep. 2010. PMID: 20356461
-
Def-6, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rac1, interacts with the skeletal muscle integrin chain alpha7A and influences myoblast differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2007 May 25;282(21):15730-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611197200. Epub 2007 Apr 2. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17403664
-
Rac1 Activation Caused by Membrane Translocation of a Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor in Akt2-Mediated Insulin Signaling in Mouse Skeletal Muscle.PLoS One. 2016 May 10;11(5):e0155292. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155292. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27163697 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CrkII Signaling in RANKL-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation and Function.J Immunol. 2016 Feb 1;196(3):1123-31. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501998. Epub 2015 Dec 22. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26695370
-
A direct interaction between JNK1 and CrkII is critical for Rac1-induced JNK activation.EMBO J. 2001 Jul 2;20(13):3437-46. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.13.3437. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11432831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han SJ, Lee JH, Choi KY, Hong SH. Novel p104 protein regulates cell proliferation through PI3K inhibition and p27Kip1 expression. BMB Reports. 2010;43(3):199–204. - PubMed
-
- Heasman SJ, Ridley AJ. Mammalian Rho GTPases: new insights into their functions from in vivo studies. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2008;9(9):690–701. - PubMed
-
- Hall A. Rho GTpases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science. 1998;279(5350):509–514. - PubMed
-
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990;249(4969):635–640. - PubMed
-
- Fukumoto Y, Kaibuchi K, Hori Y, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel type of regulatory protein (GDI) for the rho proteins, ras p21-like small GTP-binding proteins. Oncogene. 1990;5(9):1321–1328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

