MT-7716, a novel selective nonpeptidergic NOP receptor agonist, effectively blocks ethanol-induced increase in GABAergic transmission in the rat central amygdala
- PMID: 24600360
- PMCID: PMC3927450
- DOI: 10.3389/fnint.2014.00018
MT-7716, a novel selective nonpeptidergic NOP receptor agonist, effectively blocks ethanol-induced increase in GABAergic transmission in the rat central amygdala
Abstract
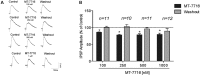
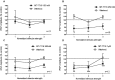
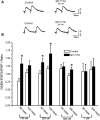
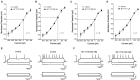
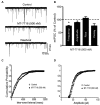
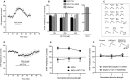
The GABAergic system in the central amygdala (CeA) plays a major role in ethanol dependence and the anxiogenic-like response to ethanol withdrawal. A large body of evidence shows that Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) regulates ethanol intake and anxiety-like behavior. In the rat, ethanol significantly augments CeA GABA release, whereas N/OFQ diminishes it. Using electrophysiological techniques in an in vitro slice preparation, in this study we investigated the effects of a nonpeptidergic NOP receptor agonist, MT-7716 [(R)-2-3-[1-(Acenaphthen-1-yl)piperidin-4-yl]-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzimidazol-1-yl-N-methylacetamide hydrochloride hydrate], and its interaction with ethanol on GABAergic transmission in CeA slices of naïve rats. We found that MT-7716 dose-dependently (100-1000 nM) diminished evoked GABAA receptor-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) and increased paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) ratio of these evoked IPSPs, suggesting a presynaptic site of action of the MT-7716 by decreasing GABA release at CeA synapses. The presynaptic action of MT-7716 was also supported by the significant decrease in the frequency of miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) induced by the nociceptin receptor (NOP) agonist. Interestingly, MT-7716 prevented the ethanol-induced augmentation of evoked IPSPs. A putative selective NOP antagonist, [Nphe1]Nociceptin(1-13)NH2, totally prevented the MT-7716-induced inhibition of IPSP amplitudes indicating that MT-7716 exerts its effect through NOPs. These data provide support for an interaction between the nociceptin and GABAergic systems in the CeA and for the anti-alcohol properties of the NOP activation. The development of a synthetic nonpeptidergic NOP receptor agonist such as MT-7716 may represent a useful therapeutic target for alcoholism.
Keywords: GABA; NOP receptor; alcohol; amygdala; electrophysiology; nociceptin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ decreases glutamate transmission and blocks ethanol-induced effects in the central amygdala of naive and ethanol-dependent rats.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014 Apr;39(5):1081-92. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.308. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24169802 Free PMC article.
-
The biology of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) related to obesity, stress, anxiety, mood, and drug dependence.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Mar;141(3):283-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24189487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ blockade of corticotropin-releasing factor-induced gamma-aminobutyric acid release in central amygdala is enhanced after chronic ethanol exposure.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Apr 15;71(8):666-76. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.10.032. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22153590 Free PMC article.
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ presynaptically decreases GABAergic transmission and blocks the ethanol-induced increase of GABA release in central amygdala.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 20;103(25):9715-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601899103. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16788074 Free PMC article.
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor antagonists as innovative antidepressant drugs.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Oct;140(1):10-25. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.05.008. Epub 2013 May 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23711793 Review.
Cited by
-
The addicted brain: understanding the neurophysiological mechanisms of addictive disorders.Front Integr Neurosci. 2015 Mar 19;9:18. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2015.00018. eCollection 2015. Front Integr Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25852502 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Subregional Differences in Alcohol Modulation of Central Amygdala Neurocircuitry.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Jul 5;15:888345. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.888345. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35866156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of stimulation of mu opioid and nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide (NOP) receptors on alcohol drinking in rhesus monkeys.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 Jul;44(8):1476-1484. doi: 10.1038/s41386-019-0390-z. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30970376 Free PMC article.
-
Driving the Downward Spiral: Alcohol-Induced Dysregulation of Extended Amygdala Circuits and Negative Affect.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019 Oct;43(10):2000-2013. doi: 10.1111/acer.14178. Epub 2019 Aug 30. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019. PMID: 31403699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Panicolytic-like effects caused by substantia nigra pars reticulata pretreatment with low doses of endomorphin-1 and high doses of CTOP or the NOP receptors antagonist JTC-801 in male Rattus norvegicus.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Oct;234(20):3009-3025. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4678-6. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28856406
References
-
- Allison S., Sheehy T. W. (1992). Alcohol: yesterday and today have we changed? Ala. Med. 61, 13–14, 16, 18. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen M., Hablitz J. J. (1994). Paired-pulse facilitation in the dentate gyrus: a patch-clamp study in rat hippocampus in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 72, 326–336 - PubMed
-
- Aujla H., Cannarsa R., Romualdi P., Ciccocioppo R., Martin-Fardon R., Weiss F. (2013). Modification of anxiety-like behaviors by nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) and time-dependent changes in N/OFQ-NOP gene expression following ethanol withdrawal. Addict. Biol. 18, 467–479 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2012.00466.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Braconi S., Sidhpura N., Aujla H., Martin-Fardon R., Weiss F., Ciccocioppo R. (2010). Revisiting intragastric ethanol intubation as a dependence induction method for studies of ethanol reward and motivation in rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 34, 538–544 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01119.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

