Sublingual microcirculation in pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 24601682
- PMCID: PMC4225801
- DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201308-277OC
Sublingual microcirculation in pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
Rationale: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a pulmonary vasculopathy that leads to failure of the right ventricle and premature death.
Objectives: To determine whether the sublingual microcirculation is affected in patients with PAH compared with healthy age- and sex-matched control subjects.
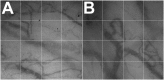
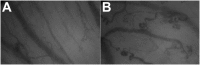
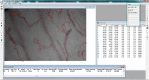
Methods: Using the CapiScope Handheld Video Capillaroscope we measured the sublingual microvasculature density, flow index, tortuosity, and curvature. Videos were acquired immediately after right heart catheterization, and determinations were made off-line by investigators blinded to the group assignment or hemodynamics.
Measurements and main results: In this cross-sectional pilot study, we included 26 patients with PAH (age, mean ± SD, 56.7 ± 10 yr; 77% women) and 14 healthy control subjects (age, 53.1 ± 12 yr; 71% women). Sublingual microvasculature flow index was lower (2 ± 0.66 vs. 2.7 ± 0.37, P < 0.001) with higher heterogeneity index (0.63 ± 0.63 vs. 0.25 ± 0.25, P = 0.04) in patients with PAH than control subjects. Microvasculature density was similar between the groups, but tortuosity was more pronounced in patients than control subjects (tort 0: 45 ± 19 vs. 23.6 ± 12, P = 0.001 and tort 1: 0.2 ± 0.16 vs. 0.06 ± 0.04, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Patients with PAH showed lower sublingual microvasculature flow index and higher tortuosity compared with healthy age- and sex-matched control subjects. Further investigations are needed to assess whether this methodology can provide information on disease prognosis and/or response to therapy in this condition.
Figures

Comment in
-
The other vascular beds in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Surrogates or associated?Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2014 May;11(4):596-7. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201402-078ED. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2014. PMID: 24828802 No abstract available.
References
-
- McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, Mathier MA, McGoon MD, Park MH, Rosenson RS, et al. American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents; American Heart Association; American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc; Pulmonary Hypertension Association. ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc.; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:1573–1619. - PubMed
-
- Badesch DB, Champion HC, Sanchez MA, Hoeper MM, Loyd JE, Manes A, McGoon M, Naeije R, Olschewski H, Oudiz RJ, et al. Diagnosis and assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:S55–S66. - PubMed
-
- Goedhart PT, Khalilzada M, Bezemer R, Merza J, Ince C. Sidestream Dark Field (SDF) imaging: a novel stroboscopic LED ring-based imaging modality for clinical assessment of the microcirculation. Opt Express. 2007;15:15101–15114. - PubMed
-
- Hubble SM, Kyte HL, Gooding K, Shore AC. Variability in sublingual microvessel density and flow measurements in healthy volunteers. Microcirculation. 2009;16:183–191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

