Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature review: IUPHAR Review 8
- PMID: 24602016
- PMCID: PMC4128058
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12678
Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature review: IUPHAR Review 8
Abstract
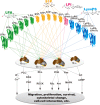
Lysophospholipids encompass a diverse range of small, membrane-derived phospholipids that act as extracellular signals. The signalling properties are mediated by 7-transmembrane GPCRs, constituent members of which have continued to be identified after their initial discovery in the mid-1990s. Here we briefly review this class of receptors, with a particular emphasis on their protein and gene nomenclatures that reflect their cognate ligands. There are six lysophospholipid receptors that interact with lysophosphatidic acid (LPA): protein names LPA1 - LPA6 and italicized gene names LPAR1-LPAR6 (human) and Lpar1-Lpar6 (non-human). There are five sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptors: protein names S1P1 -S1P5 and italicized gene names S1PR1-S1PR5 (human) and S1pr1-S1pr5 (non-human). Recent additions to the lysophospholipid receptor family have resulted in the proposed names for a lysophosphatidyl inositol (LPI) receptor - protein name LPI1 and gene name LPIR1 (human) and Lpir1 (non-human) - and three lysophosphatidyl serine receptors - protein names LyPS1 , LyPS2 , LyPS3 and gene names LYPSR1-LYPSR3 (human) and Lypsr1-Lypsr3 (non-human) along with a variant form that does not appear to exist in humans that is provisionally named LyPS2L . This nomenclature incorporates previous recommendations from the International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, the Human Genome Organization, the Gene Nomenclature Committee, and the Mouse Genome Informatix.
Keywords: FTY720 (fingolimod); G protein-coupled receptors; lipid mediators; lysophospholipids; molecular pharamacology.
© 2014 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander SPH, Benson HE, Faccenda E, Pawson AJ, Sharman JL, McGrath JC, et al. The concise guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2013/14: overview. Br J Pharmacol. 2013a;170:1449–1458.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

